Fig. 3.
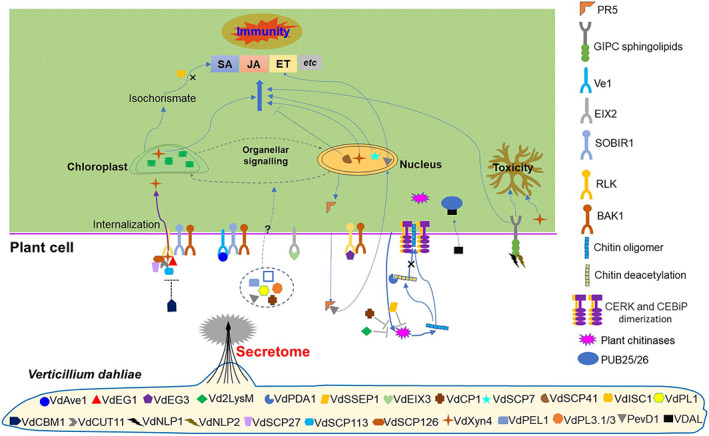
Verticillium dahliae employs its secretome to manipulate host immunity and interfere with hormone homeostasis. See Table 1 for V. dahliae protein names. VdAve1 is recognized as an avirulence determinant by tomato plants that carry the corresponding Ve1 immune receptor. VdEG1 and VdEG3 are glycoside hydrolase 12 proteins that trigger immunity dependent on the LRR‐RLPs/SOBIR1/BAK1 and LRR‐RLKs/BAK1 complexes, respectively. Vd2LysM binds long‐ or short‐chain chitin oligomers and prevents degradation of chitin by plant chitinase. VdPDA1 directs deacetylation of chitin oligomers and inhibits perception by host LysM‐containing receptors, thus avoiding ligand‐triggered immunity. VdSSEP1 hydrolyses cotton Chi28 directly, inhibiting the production of chitin oligomers. VdEIX3 exhibits immunity‐inducing activity in Nicotiana benthamiana, recognized by the leucine‐rich repeat receptor‐like protein NbEIX2. VdCP1 protects the V. dahliae cell wall from chitinase degradation. VdSCP7 targets the host nucleus to modulate plant immunity. VdSCP41 targets the plant‐specific transcription factors CBP60g and SARD1 to modulate immunity. VdISC1 disrupts the plant salicylate metabolism pathway by suppressing the transformation from isochorismate to salicylic acid. VdPL1 plays a virulence function during infection of cotton. VdCBM1 suppresses VdEG1‐, VdEG3‐, VdSCP27‐, VdSCP113‐, VdSCP126‐, VdCUT11‐ and VdXyn4‐induced cell death and some PAMPs‐triggered immunity in N. benthamiana. VdCUT11 induces plant defence responses in N. benthamania in a BAK1‐ and SOBIR1‐dependent manner. VdNLP1 and VdNLP2 are GIPC sphingolipids that act as NLP toxin receptors; NLPs form complexes with terminal monomeric hexose moieties of GIPCs and insert into the plant plasma membrane, causing cell lysis. VdSCP27, VdSCP113 and VdSCP126 induce defence responses in N. benthamania in a BAK1‐ and SOBIR1‐dependent manner. VdXyn4 plays a cytotoxic function and induces a necrosis phenotype in N. benthamania, depending on simultaneous localization to the nuclei and chloroplasts in a BAK1‐ and SOBIR1‐dependent manner. VdPEL1 exhibits pectin hydrolytic activity and induces cell death in plants. VdPL3.1/3 have virulence functions during infection of cotton. PevD1 induces ethylene biosynthesis by directly binding to ORE1. VDAL protects transcription factor MYB6 from degradation by interacting with the E3 ligases PUB25 and PUB26 to enhance Verticillium wilt resistance. BAK1, LRR‐RLK BRI1‐associated kinase‐1; CBP60g, calmodulin binding protein 60 family member g; CEBiP, chitin‐elicitor binding protein; CERK, receptor chitin elicitor receptor kinase; Chi28, chitinase 28; EIX2, leucine‐rich repeat receptor‐like protein; ET, ethylene; GIPC, glycosylinositol phosphorylceramide; JA, jasmonic acid; LRR, leucine‐rich repeat; LysM, lysin motif; MYB6, MYB domain protein 6; NLP, necrosis‐ and ethylene‐inducing‐like protein; ORE1, A senescence‐associated NAC transcription factor; PAMP, pathogen‐associated molecular pattern; PR5, pathogenesis‐related protein 5 (PR5)‐like protein; PUB25/26, plant U‐box 25/26; RLK, receptor‐like kinase; RLP, receptor‐like protein; SA, salicylic acid; SARD1, systemic acquired resistance deficient 1; SOBIR1, LRR‐RLK suppressor of BIR1‐1; Ve1, leucine‐rich repeat receptor‐like protein.
