Figure 4.
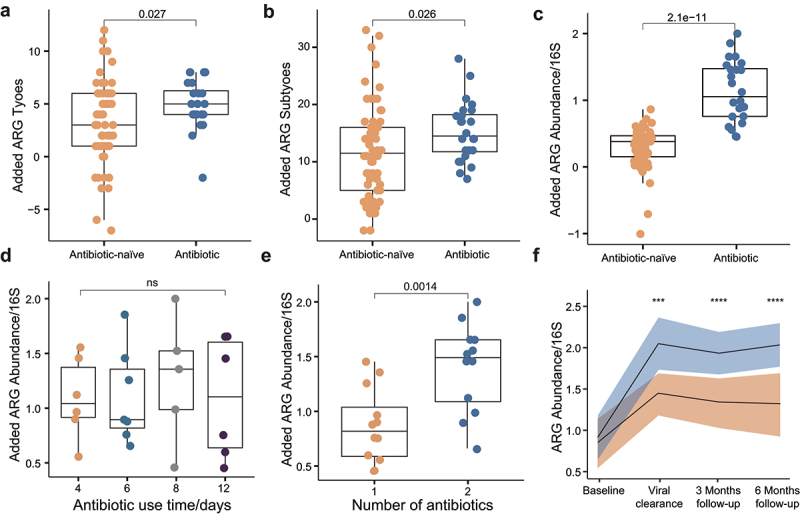
Antibiotics further expand the resistome in COVID-19 patients. The increment of the observed ARG types (a), subtypes (b), and abundance (c) in antibiotic-naive COVID-19 patients is significantly higher than that of antibiotic-experienced COVID-19 patients. Increment refers to the expansion of resistome from baseline to viral clearance. (d) The increment of ARGs abundance in antibiotic-experienced COVID-19 patients is not associated with the length of antibiotic use time. (e) The increment of ARGs abundance in subjects who received two antibiotics is significantly higher than that of subjects who received one antibiotic. (f) Dynamics of ARGs abundance in antibiotic-naive COVID-19 patients and antibiotic-experienced COVID-19 patients. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, ****P < .0001, Kruskal–Wallis and Dunn’s tests (all panels).
