Figure 5.
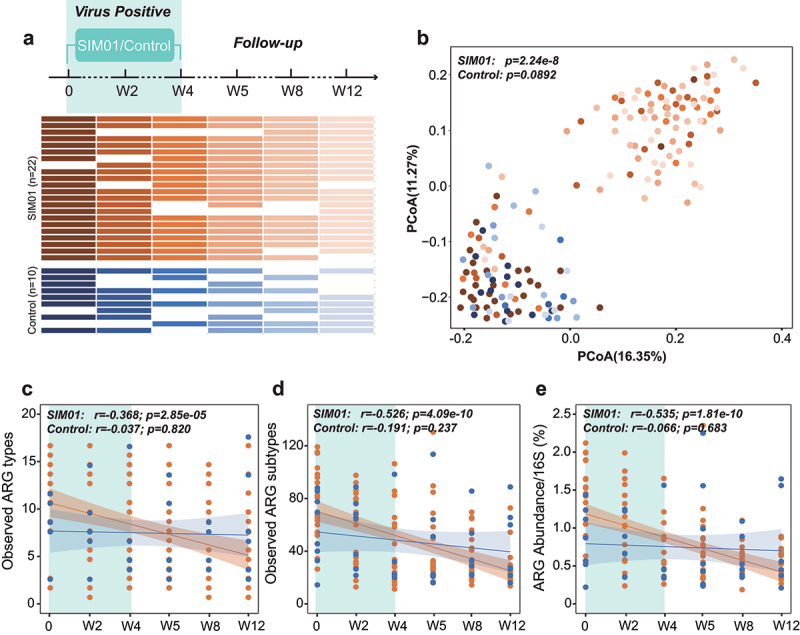
Probiotics reduce ARGs in COVID-19 patients during virus-positive period. (a) Schematic overview of the study design, depicting the total number of samples and participants from whom data were available. The horizontal bars represent the sample collected at specific time point. (b) Probiotics were associated with an increased dissimilarity of resistome configuration compared with pre-treatment ARGs. The observed ARG types (c), subtypes (d), and abundance (e) in COVID-19 patients exhibited significant decrease after taking probiotics, but no significant trend was found in control group (Pearson Correlation).
