FIGURE 3.
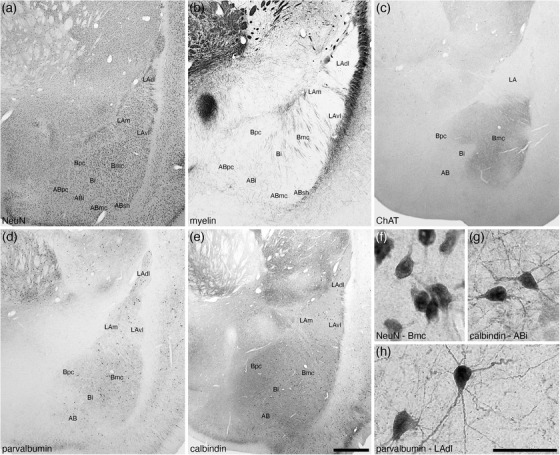
Low (a–e) and high (f–h) magnification photomicrographs of the basolateral nuclear complex within the amygdaloid body of the tree pangolin stained for neuronal nuclear marker, NeuN (a, f), myelin (b), cholineacetyltransferase, ChAT (c), parvalbumin (d, h), and calbindin (e, g). Within the lateral amygdaloid nucleus (LA), we identified the dorsolateral (LAdl), medial (LAm), and ventrolateral (LAvl) parts. Within the basal amygdaloid nucleus, we identified the magnocellular (Bmc), intermediate (Bi), and parvocellular (Bpc) divisions, and within the accessory basal nucleus (AB), we identified the intermediate (ABi), magnocellular (ABmc), parvocellular (ABpc), and shell (ABsh) divisions. Certain stains were specific to particular nuclei, such as the intense ChAT neuropil staining (c) in the Bmc. Images (f) and (g) show examples of neural morphology in the (f) Bmc, NeuN immunostaining, (g) ABi, calbindin immunostaining, (h) LAdl, parvalbumin immunostaining. In all images, dorsal is to the top and medial to the left. Scale bar in (e) = 1 mm and applies to (a)–(e). Scale bar in (h) = 250 μm and applies to (f)–(h). See list for abbreviations
