Fig. 2.
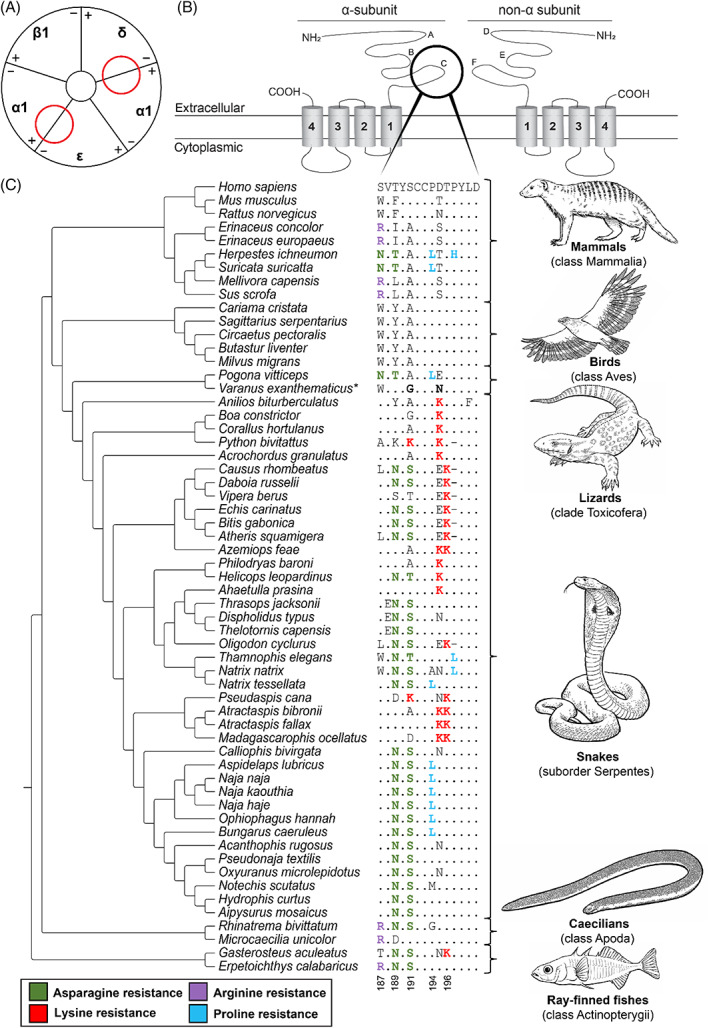
Convergent evolution of α‐neurotoxin resistance in animals. (A) Schematic representation (based on Kini, 2019) of the α‐1 muscle‐type nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR). Red circles indicate the position of the ligand‐binding domain of α‐neurotoxins in the nAChR. (B) Protein topology of an α‐subunit and a non‐α‐subunit of the muscle‐type nAChR. A–F indicate the loop structures at the extracellular domain in the respective subunits (Rahman et al., 2020). The black circle indicates the C‐loop involved in α‐neurotoxin binding. (C) Sequence alignment of the α1‐nAChR ligand‐binding domain. The reference amino acid sequence is from humans (Homo sapiens) and differences from this sequence are displayed for all other species. Substitutions associated with resistance are highlighted in coloured font. The asterisk (*) in Varanus exanthematicus indicates that the two substitutions shown are associated with reduced binding affinity (Jones, Harris & Fry, 2021). Tree topology based on Khan et al. (2020). Sequence accession numbers are provided in Table S5.
