FIGURE 7.
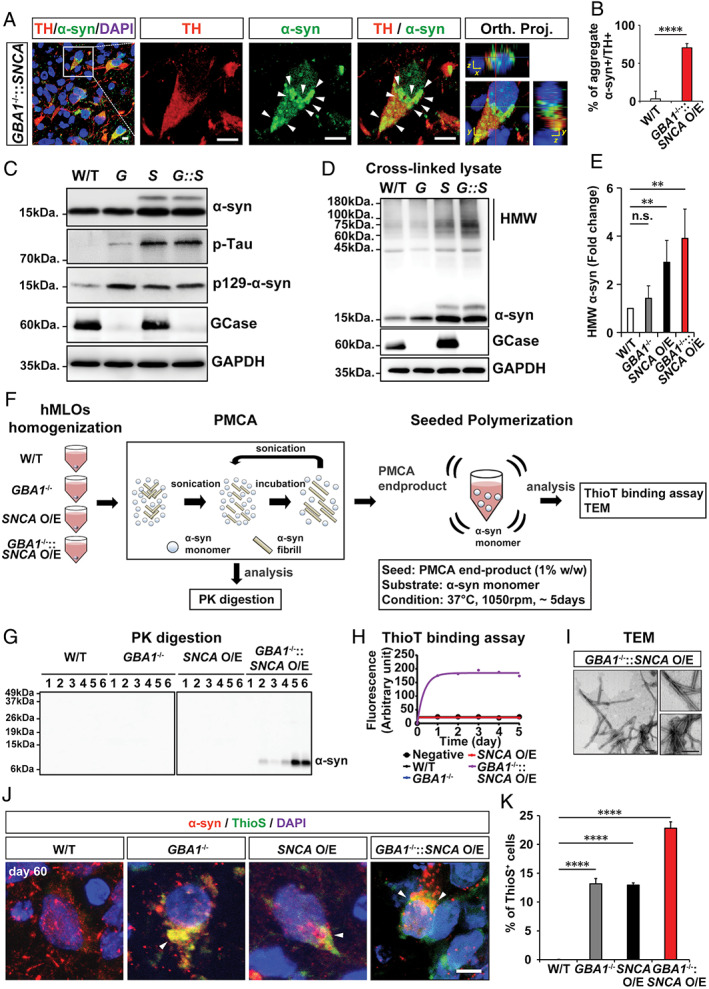
α‐Synuclein (α‐syn) aggregates from GBA1 −/−::SNCA overexpressing (O/E) human midbrain‐like organoids (hMLOs) are pathogenic. (A) Cryosections of GBA1 −/−::SNCA O/E hMLOs at day 60 stained with specific antibodies against tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and α‐syn. The merged images show orthogonal Z‐stack projections (Orth. Proj.). Scale bars = 10μm. (B) Quantification of the percentages of TH+ cells with α‐syn aggregates. The percentage of TH+ cells containing aggregate α‐syn is shown (mean ± standard error of the mean [SEM]; ****p < 0.0001; n = 3). (C) Western blots of α‐syn, p‐Tau, p129‐α‐syn, and glucocerebrosidase (GCase) proteins in day 60 hMLOs derived from wild‐type (W/T), GBA1 −/− (G), SNCA O/E (S), and GBA1 −/−::SNCA O/E ESCs. Glyceraldehyde‐3‐phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as a loading control. (D) Western blotting was performed to detect high‐molecular‐weight (HMW) α‐syn. H9 isogenic hMLOs were subjected to 1mM disuccinimidyl glutarate cross‐linking before whole lysates were extracted. (E) Quantification of HMW α‐syn from the experiment in D (mean ± SEM; n.s. = no significance, **p < 0.005; n = 4). (F) Schematic representation of protein misfolding cyclic amplification (PMCA) and seeded polymerization for the thioflavin T (ThioT) binding assay and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) imaging. (G) Proteinase K (PK) digestion patterns of PMCA products from day 60 hMLOs. (H) ThioT binding kinetics of seeded polymerization using PMCA end products for each type of hMLO. (I) TEM images of seeded aggregates. Scale bars = 200nm. (J) Immunostaining for α‐syn and thioflavin S (ThioS) double‐positive neurons from control, GBA1 −/−, SNCA O/E, and GBA1 −/−::SNCA O/E hMLOs at day 60. The arrowheads point to the colocalization of α‐syn and ThioS. Scale bar = 5μm. (K) Quantification of the immunostaining from J (mean ± SEM; ****p < 0.0001; n = 3). DAPI = 4,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole. [Color figure can be viewed at www.annalsofneurology.org]
