FIGURE 5.
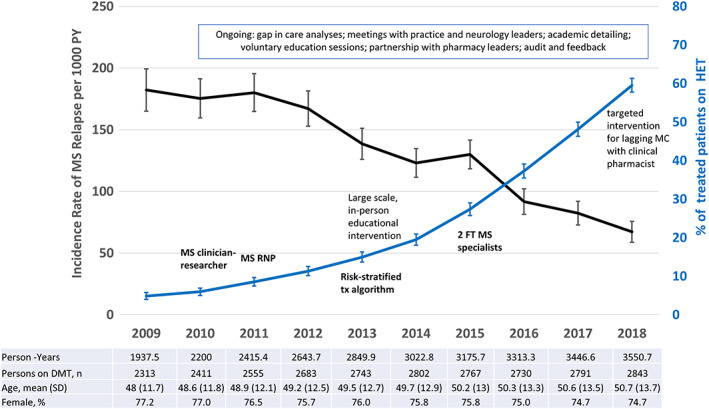
Multiple sclerosis (MS) program implementation, highly effective disease‐modifying treatments (DMTs), and MS relapses. Depicted are the key milestones of the multicomponent MS intervention (in text), the annual proportion of MS patients treated with highly effective DMTs (HETs) among persons treated with any DMT with 95% confidence intervals (CIs; blue line, right vertical axis) and the annual MS relapse rate (ARR) per 1,000 person‐years with 95% CI (black line, left vertical access) among MS DMT‐treated patients. The figure shows that the increase in use of HETs corresponds to a decrease in the ARR and that both accelerated in 2015 corresponding with the hiring of 2 additional MS specialists. A targeted intervention for a large medical center (MC) that lagged in adopting the MS Treatment Optimization Program began in September of 2017 and included series of local education sessions for neurologists and training of a clinical pharmacist supervised by an MS specialist remotely. MS ARR was stable prior to implementation (2009–2011), and declined by 69.0% (95% CI = 64.1–73.2%, p < 0.0001, adjusted for age and sex) between 2011 and 2018. FT = full time; SD = standard deviation; RNP = registered nurse practitioner; tx = treatment.
