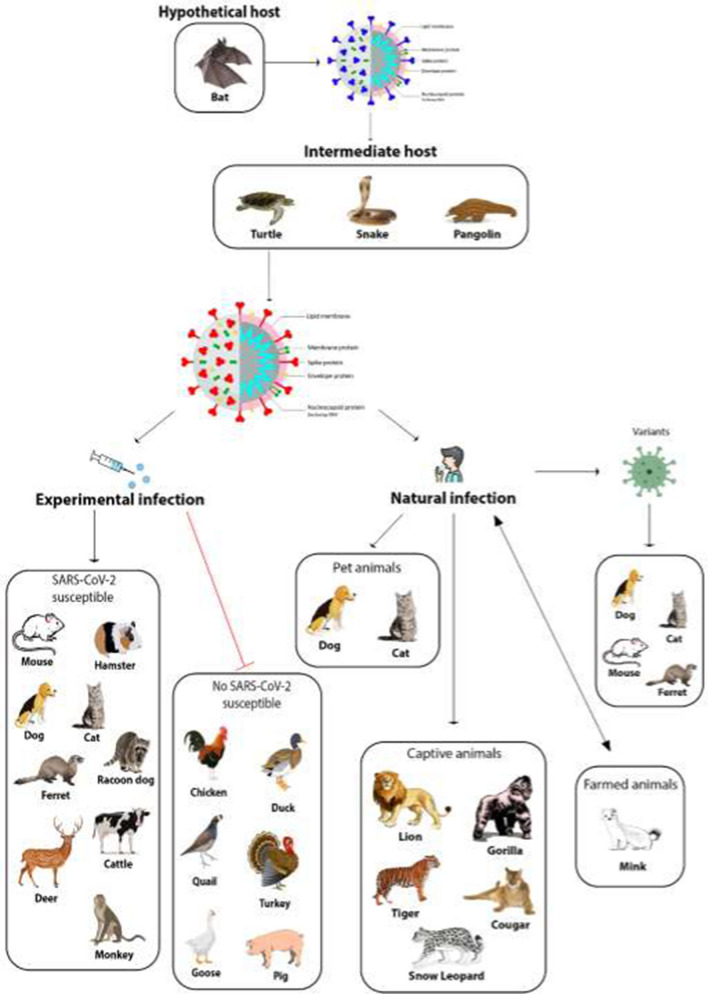
Fig. 1.
SARS-CoV-2 transmission among different animals. The most widely accepted hypothesis is that SARS-CoV-2 was derived from a bat coronavirus after a modification in a putative intermediate host, where it acquired the capability to infect humans. The wide circulation of the virus among humans caused a pandemic, and it is plausible that infected humans may have transmitted the virus to different animal species. In order to better understand the role of animals in the epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 and to establish appropriate animal models, several species have been experimentally infected, but not all of them were found to be permissive for the infection. To date, only minks seem to be able to transmit SARS-CoV-2 infection to humans. Greater attention should be devoted to monitoring new variants of SARS-CoV-2 because of their potential to acquire the ability to infect domestic or wild animals, which could potentially serve as reservoirs for the virus.