Fig. 1.
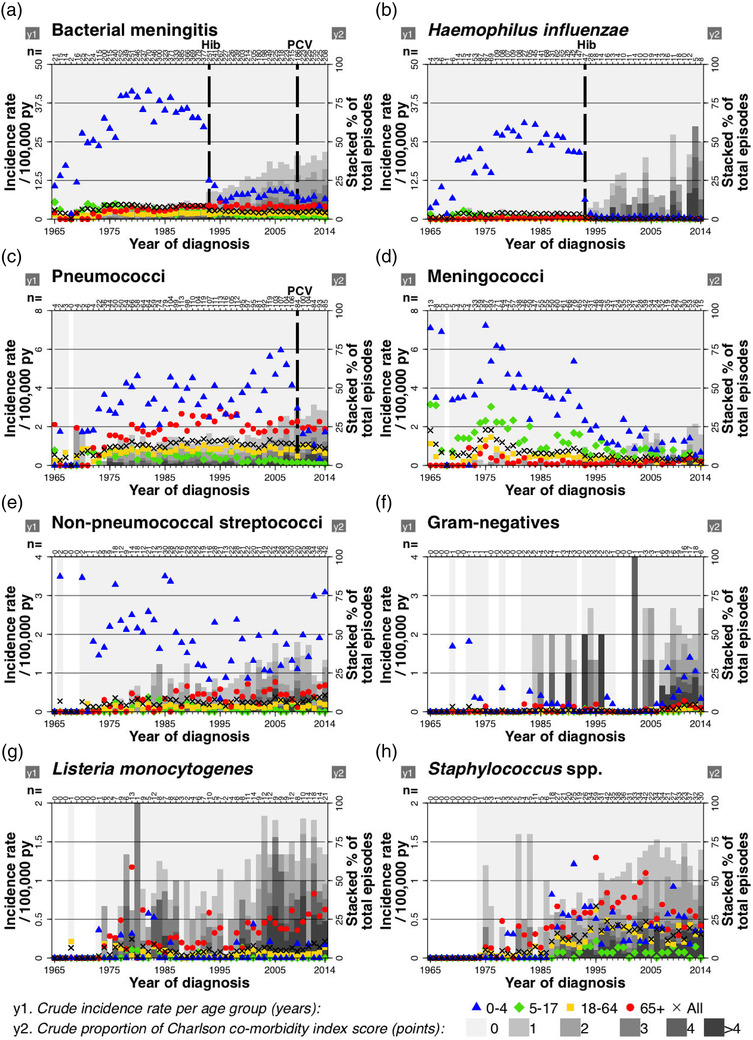
Incidence rate (IR) of and comorbidity with bacterial meningitis (BM). The annual IRs of BM in Sweden between 1965 and 2014 by single pathogen and age group are shown in relation to the introduction of H. influenzae B (Hib) and pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs) on the left y‐axis (y1) and annual stacked proportions of patient Charlson comorbidity index scores on the right y‐axis (y2) in grayscale. The total annual number of episodes is shown for each year. The annual incidence of (a) all BM, followed by that of BM due to single pathogens, namely (b) Haemophilus influenzae, (c) Streptococcus pneumoniae, (d) Neisseria meningitidis, (e) non‐pneumococcal streptococci, (f) gram‐negative bacteria, (g) Listeria monocytogenes and (h) Staphylococcal spp.
