FIGURE 3.
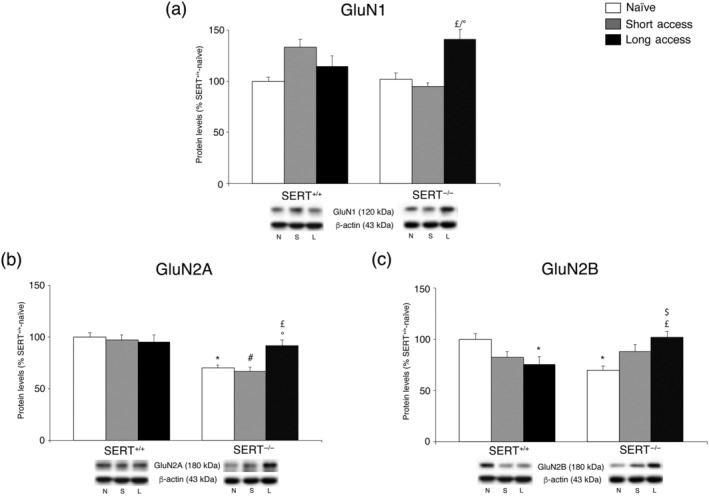
Interaction between SERT deletion and cocaine self‐administration (short or long access) on the NMDA receptor subunits in the core nucleus accumbens. Protein levels of GluN1 (a), GluN2A (b) and GluN2B (c) in core nucleus accumbens are expressed as percentages of SERT+/+‐naive rats. In panel (d), representative immunoblots are shown for GluN2A (180 kDa), GluN2B (180 kDa), GluN1 (120 kDa) and β‐actin (43 kDa) proteins. Histograms represent the mean ± SEM of the following number of rats: naïve (SERT+/+ n = 7; SERT−/− n = 7), short access (SERT+/+ n = 6; SERT−/− n = 6) and long access (SERT+/+ n = 7; SERT−/− n = 7). *P < .05 versus SERT+/+‐naive; # P < .05 versus SERT+/+‐ short access; $ P < .05 versus SERT+/+‐short access; £ P < .05, £ P < .05 versus SERT−/−‐naive; °P < .05 versus SERT−/−‐short access (Tukey's multiple comparisons test). N, naïve; S, Cocaine Short‐Access; L, Cocaine Long‐Access
