Figure 4.
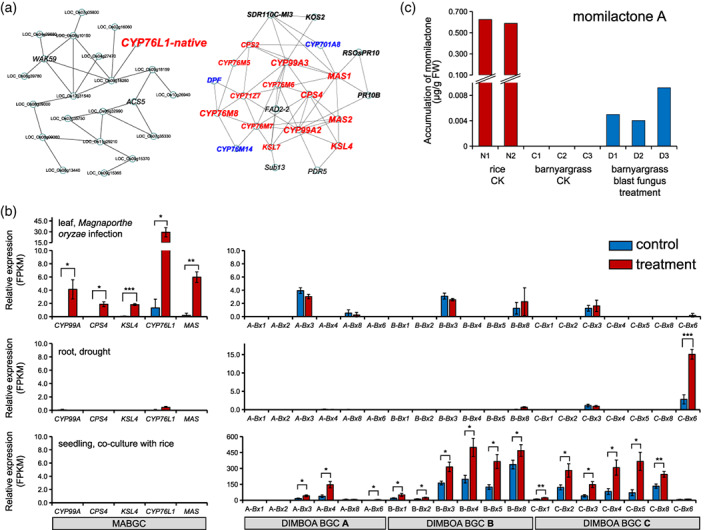
Expression profiling of clusters of momilactone A biosynthetic genes (MABGCs) from rice (Oryza sativa) and barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus‐galli).
(a) Gene co‐expression network of native CYP76L1 (CYP76L1‐native) reveals the independent relationship between CYP76L1‐native and the momilactone biosynthetic genes in rice.
(b) Transcriptomic profiling of barnyardgrass (E. crus‐galli) MABGC and the gene clusters for DIMBOA biosynthesis (Bx clusters and Bx6 genes from three subgenomes) in response to blast pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae inoculation, drought, and co‐culture with rice. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, Student's t‐test.
(c) Comparison of momilactone A accumulation in leaves from rice (O. sativa) and barnyardgrass (E. crus‐galli) under control (CK) and blast fungus M. oryzae infection conditions. N1–N2, C1–C3, and D1–D3 are biological replicates of the three experiments. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
