FIGURE 1.
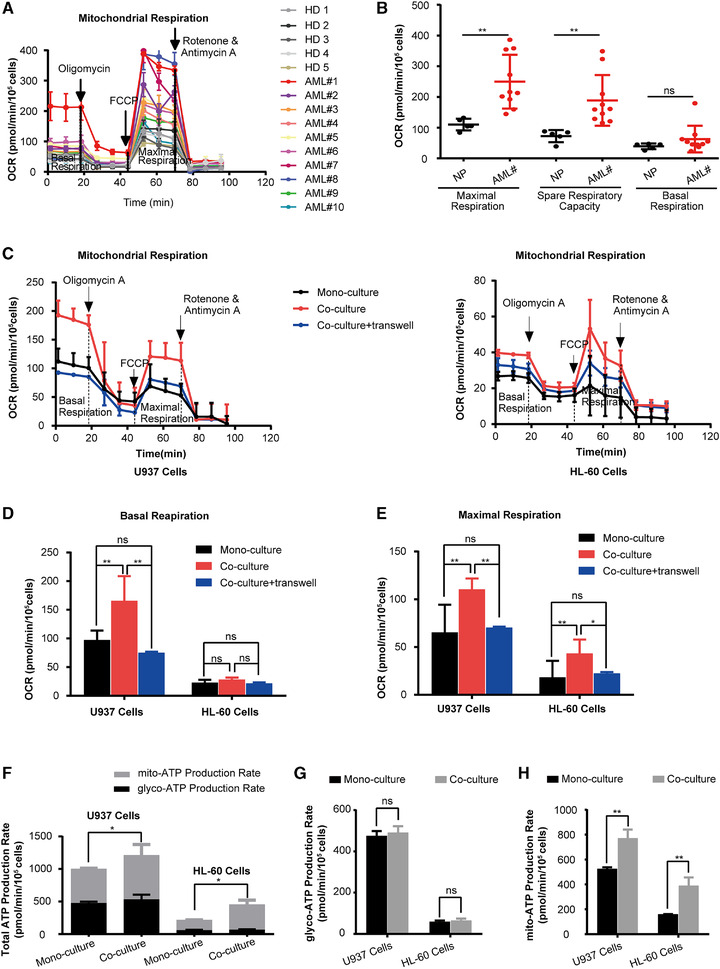
Coculture of AML cells with HS‐5 cells exhibited higher OXPHOS activity and increased ATP synthesis. (A) Sequential injections of oligomycin, FCCP, and rotenone/antimycin were used to obtain mitochondrial respiration dynamics of CD34+ cells from the BM of AML patients and healthy donors (n = 10 for AML patients; n = 5 for healthy donors). (B) The mitochondrial basal respiration, maximal respiration, and spare respiratory capacity of CD34+ cells from the BM of AML patients and healthy donors were analyzed with cell numbers normalized. (C) Sequential administration of oligomycin, FCCP, and rotenone/antimycin were used to obtain mitochondrial respiration dynamics of AML cells. (D‐E) AML cells were cultured with HS‐5 cells in a contact or non‐contact co‐culture system and then the mitochondrial basal and maximal respiration of AML cells were analyzed with cell numbers normalized. (F‐H) AML cells were cultured with or without HS‐5 cells and then the ATP production Capacity was analyzed with cell numbers normalized. (F) Total ATP production rate, (G) glycolytic, and (H) mitochondrial ATP production rates in AML cells. The data represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments with 3 replicates for each experiment. AML#, AML patients; HD, healthy donors. ns, no significant difference, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001
