FIGURE 4.
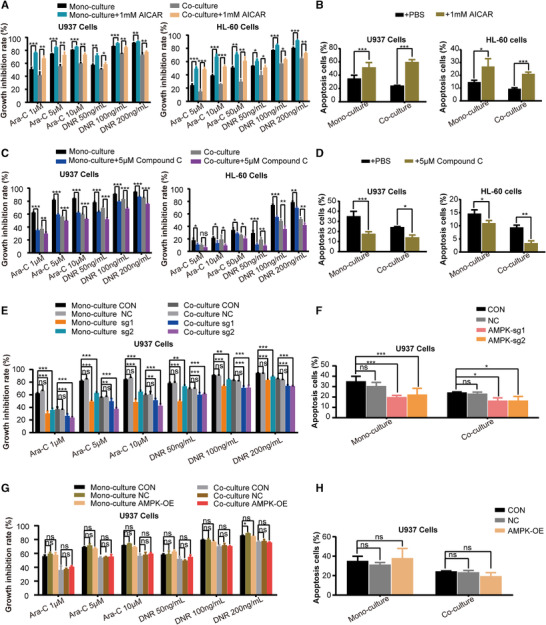
AMPK inhibition mediated the chemoresistance of AML cells induced by HS‐5 cells. (A) Growth inhibitory effect of 24 h treatment with different concentrations of Ara‐C and DNR on AML cells after treatment with 1 mM 5‐aminoimidazole‐4‐carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR) was measured by CCK‐8 assay. (B) The percentage of apoptotic cells of 24 h treatment with Ara‐C (The concentration of Ara‐C was 50 μM for HL‐60 cells and 5 μM for U937 cells) on AML cells after treatment with 1 mM AICAR was expressed as mean ± SD from 3 independent experiments. (C) Growth inhibitory effect of 24 h treatment with different concentrations of Ara‐C and DNR on AML cells after treatment with 5 μM Compound C was measured by CCK‐8 assay. (D) The percentage of apoptotic cells of 24 h treatment with Ara‐C (The concentration of Ara‐C was 50 μM for HL‐60 cells and 5 μM for U937 cells) on AML cells after treatment with 5 μM Compound C was expressed as mean ± SD from 3 independent experiments. (E) Growth inhibitory effect of 24 h treatment with different concentrations of Ara‐C and DNR on U937 cells knocked out for AMPK was measured by CCK‐8 assay. (F) The percentage of apoptotic cells of 24 h treatment with Ara‐C (The concentration of Ara‐C was 50μM for HL‐60 cells and 5 μM for U937 cells) on U937 cells knocked out for AMPK was expressed as mean ± SD from 3 independent experiments. (G) Growth inhibitory effect of 24 h treatment with different concentrations of Ara‐C and DNR on AMPK‐overexpressing U937 cells. (H) The percentage of apoptotic cells of 24 h treatment with Ara‐C on AMPK‐overexpressing U937 cells was expressed as mean ± SD from 3 independent experiments. The data represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments with 3 replicates for each experiment. CON, wide type; NC, empty vector control; AMPK‐OE, AMPK overexpression; AMPK‐sg1/2, AMPK gene was knocked out. ns, no significant difference, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001
