FIGURE 2.
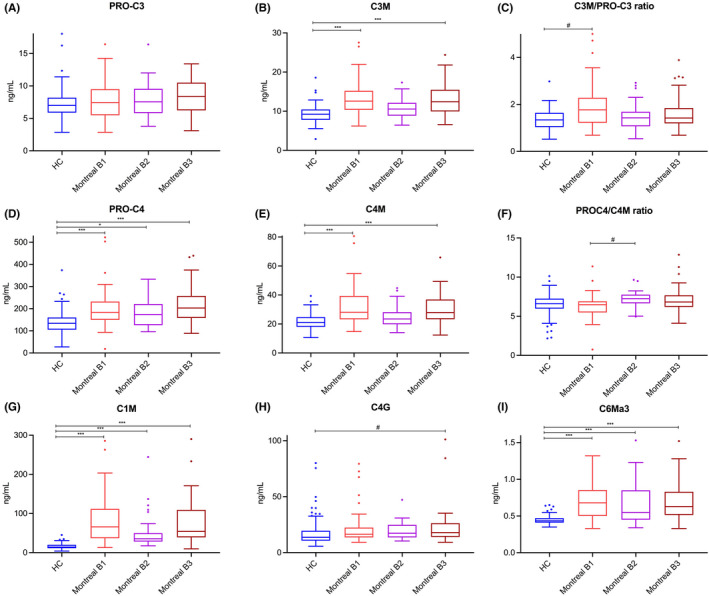
(A–I) Serum concentrations and ratios of type I (C1M), III (C3M, PRO‐C3, C3M/PRO‐C3), IV (C4M, PRO‐C4, C4G, PRO‐C4/C4M) and VI (C6Ma3) collagen formation and degradation biomarkers in patients with CD (n = 101), stratified by disease behaviour, and in healthy controls (HC, n = 96). (A–C) Serum C3M levels were significantly elevated in patients with CD compared with HC, indicating relatively increased degradation of type III collagen, whereas PRO‐C3 levels were equal among groups, resulting in a moderately elevated C3M/PRO‐C3 ratio in patients with CD compared with controls (especially in patients with non‐stricturing, non‐penetrating disease), which was however only nominally statistically significant. (D–F) Serum PRO‐C4 and C4M levels were elevated in patients with CD compared with HC, but the PRO‐C4/C4M ratio was nominally significantly elevated in patients with stricturing disease, compared with both HC and patients with non‐stricturing, non‐penetrating disease. (G) A specific fragment of MMP‐2, 9, 13‐mediated type I collagen degradation (C1M) was markedly elevated in patients with CD compared with HC. (H) Serum C4G levels were nominally significantly elevated in patients with CD, particularly in patients with penetrating CD, compared with HC. (I) Serum C6Ma3 levels were elevated in patients with CD compared with HC. Boxplots were drawn according to the Tukey method, with inner fences defined as 25th/75th percentile ±1.5 IQR. Significances were calculated from Kruskal‐Wallis tests with post‐hoc Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. #Only nominally significant, but not statistically significant after Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons.
