FIGURE 1.
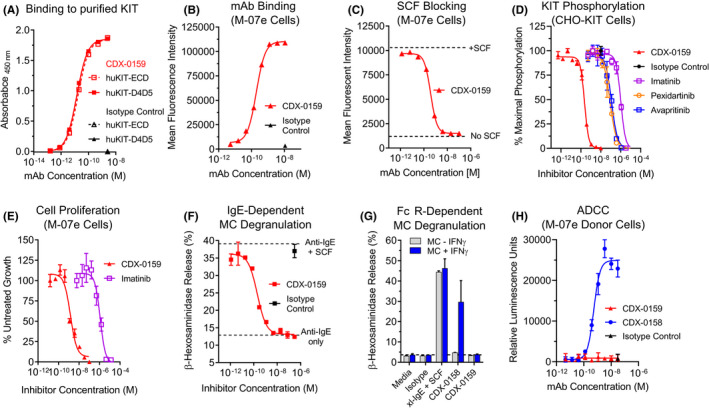
CDX‐0159 Inhibits SCF‐dependent KIT Activation and MC Degranulation. (A) CDX‐0159 binds to purified human KIT extracellular domain (huKIT‐ECD) and a fragment comprised of the membrane proximal dimerization domains Ig4 and Ig5 (huKIT‐D4D5) with indistinguishable potency. Purified KIT proteins were immobilized in ELISA plates followed by titration with CDX‐0159. (B) Binding to KIT‐expressing M‐07e cells was demonstrated by flow cytometry, with an EC50 value of 153 ± 22 pM (C). CDX‐0159 completely blocks binding of 10 nM fluorescently labeled SCF to M‐07e cells with a potency of 118 ± 6 pM. (D) Inhibition of SCF‐dependent KIT tyrosine phosphorylation in CHO cells expressing human KIT is demonstrated for CDX‐0159 and KIT‐targeting TKIs imatinib, pexidartinib, and avapritinib. (E) SCF‐dependent proliferation of M‐07E cells is inhibited by CDX‐0159 more potently than with imatinib. (F) IgE‐dependent MC degranulation as measured by β‐hexosaminidase release is significantly enhanced by addition of 100 ng/mL of SCF. CDX‐0159 fully inhibits SCF‐dependent β‐hexosaminidase release. (G) Fc‐silencing mutations in CDX‐0159 abolish FcγR‐dependent MC activation. In MCs pre‐treated with IFNγ to upregulate FcγRI, CDX‐0158 but not CDX‐0159 induces MC β‐hexosaminidase release. Cross‐linked IgE (xl‐IgE) plus SCF is used as a positive control. (H) CDX‐0159 does not elicit measurable ADCC. Fc‐silencing mutations abolish ADCC observed with CDX‐0158 using a reporter assay using Jurkat cells with an NFAT‐luciferase reporter element under the control of FcγRIII as effector cells, and M‐07e as target cells. All experiments were performed at least 3 independent times. Mean values and S.E.M.s are shown
