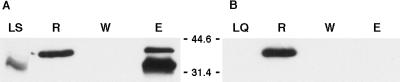
FIG. 4.
Interaction of HrpR and HrpS detected by column-binding experiments. Clarified lysate from an IPTG-induced DH5α(pREP4)(pSHS23Q30) culture expressing HrpS was loaded onto an Ni+-nitrilotriacetic acid column (Qiagen), and the column was washed as described in Materials and Methods to release weakly bound proteins. A clarified lysate from an IPTG-induced DH5α(pTSR8CTC) culture was then applied to the column, and the column was washed with sufficient buffer to produce an HrpR-free elutant. Bound proteins were eluted using 250 mM imidazole in lysis buffer. Proteins in the indicated samples were fractionated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes, and probed using anti-His and anti-FLAG antibodies simultaneously as described in Materials and Methods. (A) HrpR eluted from an HrpS-loaded column. Lane LS, DH5α(pREP4)(pSHS23Q30) lysate applied to the column (contrast enhanced); lane R, DH5α(pTSR8CTC) lysate applied to the column; lane W, final wash prior to elution; lane E; imidazole-eluted proteins. (B) HrpR binding to an E. coli protein-loaded column. Lane LQ, DH5α(pREP4)(pQE30) lysate applied to the column; lane R, DH5α(pTSR8CTC) lysate; lane W, final wash; lane E, imidazole-eluted proteins. Molecular masses shown in kilodaltons were estimated using Kaleidoscope prestained markers (Bio-Rad).