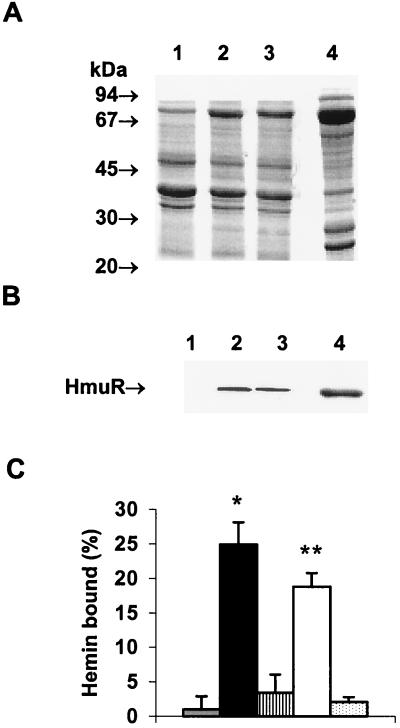
FIG. 1.
E. coli cells expressing rHmuR-6His (containing the signal sequence and the V5–six-His tag) and rHmuR (containing the signal sequence but lacking the V5–six-His tag) bind hemin. (A and B) Localization of recombinant HmuR in E. coli cells. Membrane fractions of E. coli cells harboring the vector alone (lane 1), expressing rHmuR (lane 2), expressing rHmuR-6His (lane 3), and expressing rHmuR-6His lacking the signal sequence and deposited in inclusion bodies (lane 4) were adjusted to an OD600 of 1.0, and outer membranes (lanes 1 to 3) and inclusion bodies (lane 4) were isolated. (A) SDS–12.5% PAGE gel stained with CBB (10-μl portions of the samples were loaded onto the gel). (B) Western blot developed by probing with anti-HmuR antibodies raised to the recombinant six-His-tagged protein (5-μl portions of the samples were loaded onto the gel). (C) Hemin binding to E. coli cells expressing rHmuR. E coli cells were resuspended in PBS, adjusted to an OD600 of 1.0, and incubated for 1 h at RT with 10 μM hemin. Binding was determined by the decrease in the absorbance of the supernatant at 400 nm and was recorded as the percentage of the input hemin. Three independent experiments were performed in duplicate. Data are means ± SD. Asterisk, P < 0.001 for E. coli expressing membrane-associated rHmuR-6His (black bar) versus E. coli harboring the vector alone (grey bar); double asterisks, P < 0.05 for E. coli expressing membrane-associated rHmuR (open bar) versus E. coli harboring the vector alone. E. coli expressing rHmuR-6His (striped bar) and rHmuR (dotted bar) lacking the signal sequence, both of which were deposited in inclusion bodies, is also shown.