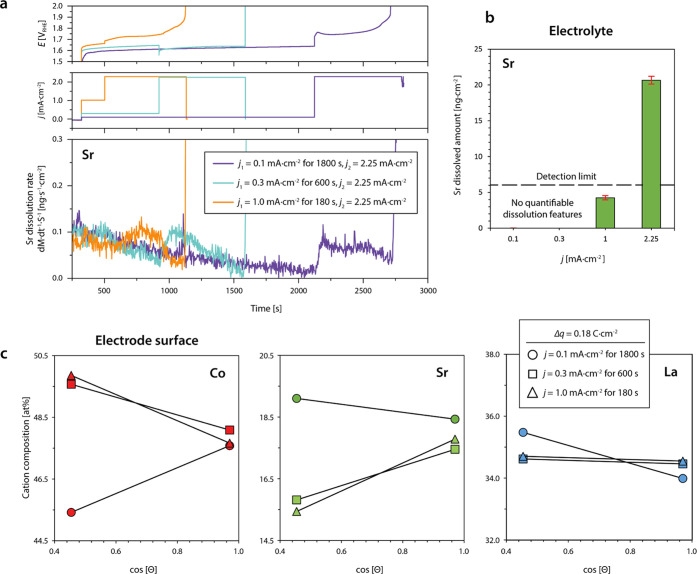
Figure 5.
Investigation of stoichiometric changes of LSCO electrocatalysts during steady-state OER operation. (a) Chemical analysis of the electrolyte by online ICP-MS measurements. The dissolution rate of Sr is monitored during three different measurement protocols. For the systematic investigation of Sr dissolution at different current densities, two galvanostatic holds are applied during each measurement protocol, respectively (j1 = 0.1, 0.3, or 1.0 mA·cm–2 and j2 = 2.25 mA·cm–2). (b) Dissolved amounts of Sr are determined for the galvanostatic holds at different current densities. Error bars represent the standard deviation of average values obtained from three measurements, each performed on a fresh catalyst surface. (c) Angle-dependent XPS analysis of the surface stoichiometry after OER operation in the low-potential regime similar to the conditions used during online ICP-MS. The depletion of strontium and the enrichment of cobalt is detected for catalysts operated at j = 0.3 and 1.0 mA·cm–2. XPS analysis was performed at a photoemission angle Θ = 15° (less surface-sensitive) and Θ = 64° (more surface-sensitive).