Figure 1.
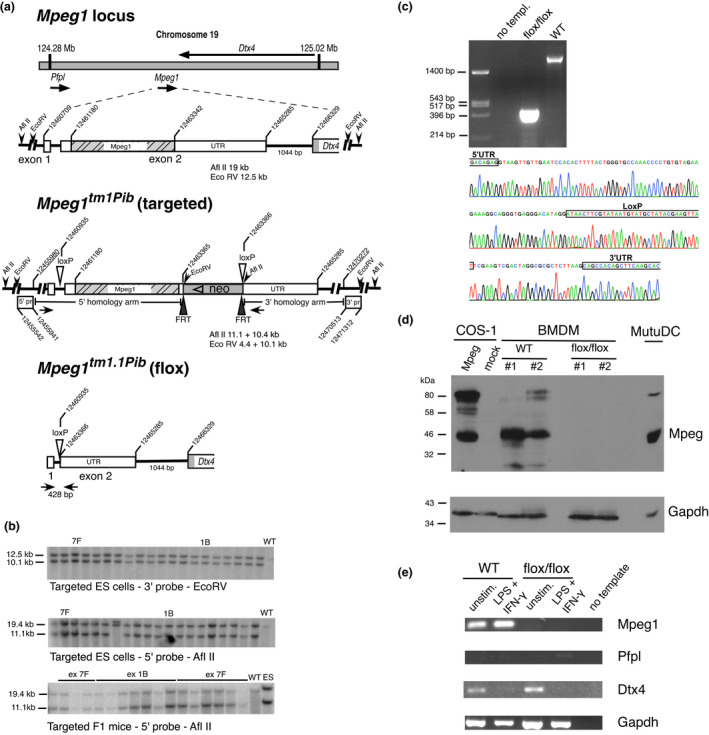
Gene targeting of Mpeg1. (a) The Mpeg1 locus, Mpeg1 structure and predicted allele structure after insertion of loxP into the 5′ UTR and the selectable marker (neo) and loxP into the 3′ UTR [Mpeg tm1Pib (targ)]. Subsequent removal of the Mpeg1 coding sequence and neomycin (neo) cassette by cre‐mediated recombination yields the knockout allele [Mpeg1 tm1.1Pib (flox)]. Sequences cloned and used as 5′ or 3′ flanking probes (pr) are indicated. Coordinates are from the mouse genomic reference sequence GRCm38.p3 C57/BL6. (b) Validation of ES cell and F1 mouse genotypes by Southern blotting. The predicted sizes of genomic fragments generated following EcoRV or AflII treatment and recognized by the indicated 5′ and 3′ probes are shown in a. (c) Validation of cre‐mediated Mpeg1 deletion in a floxed mouse. Shown is the relevant DNA sequence of the 428‐bp flox/flox PCR product amplified using the primers shown as closed arrowheads in the Mpeg1 tm1.1Pib allele shown in a. These primers yield a 2800‐bp product from WT mouse genomic DNA (upper panel). (d) Protein extracts from 106 BMDMs derived from WT or knockout (flox/flox) mice were separated by 10% SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted for Mpeg1 (1:2000 rabbit anti‐Mpeg), followed by immunoblotting for GAPDH (1:5000 anti‐GAPDH). These were compared with extracts from COS‐1 cells transiently expressing Mpeg1, and from the MutuDC line (104 cells). Image shown represents three independent experiments. (e) Total RNA from unstimulated or IFNγ‐ and LPS‐stimulated BMDMs derived from WT or knockout (flox/flox) mice was assessed via RT‐PCR for the presence of Mpeg1, Pfpl, Dtx4 and housekeeping Gapdh transcripts. ES cell, embryonic stem cell; BMDM, bone marrow‐derived macrophage; IFN, interferon; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; Mpeg1, macrophage‐expressed gene 1; SDS–PAGE, sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; RT‐PCR, reverse‐transcriptase PCR; UTR, untranslated region; WT, wild type. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
