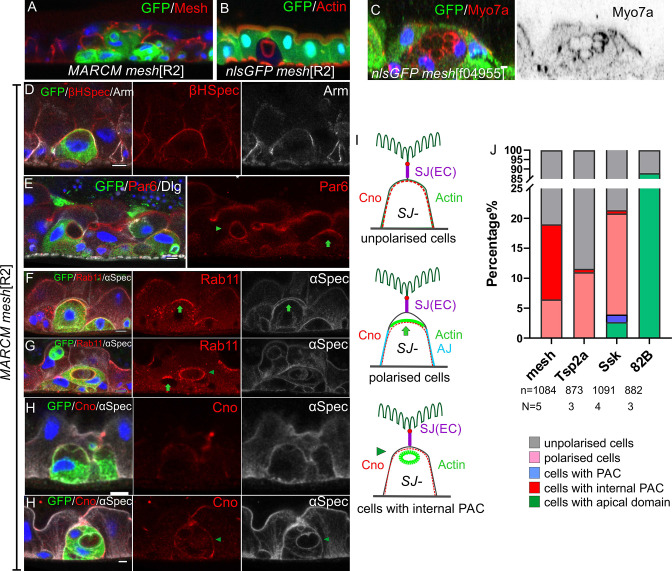
Figure 8. mesh mutants fail to form a PAC or form an internal PAC.
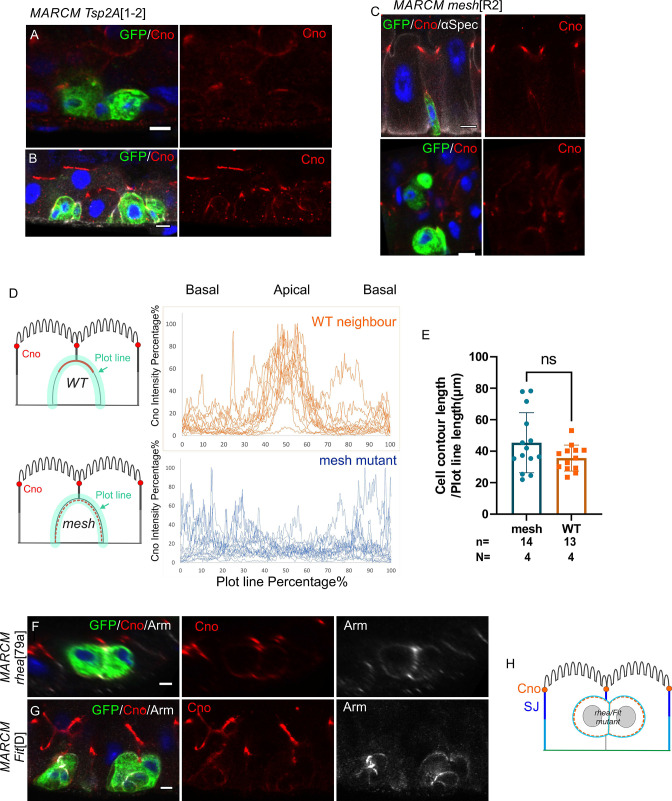
(A) A meshR2 homozygous MARCM clone marked by GFP (green). The mutant cells lack Mesh staining (red), fail to make septate junctions and do not reach the gut lumen. (B–C) meshR2 (B) and meshf04955 (C) homozygous mutant cells marked by the loss of GFP (green). The mutant cells form internal PACs that are marked by actin (red in B) and Myo7a (red in C). The cell in C has formed multiple internal PACs. (D) βH-spectrin (red) localises around the plasma membrane of meshR2 mutant enteroblasts (green), indicating that they do not polarise normally, but adherens junctions (Arm, greyscale) are still down-regulated at the apical surface. (E) meshR2 mutant enteroblasts (green) stained for Par-6 (red). Par-6 localises to the apical membrane (green arrow) in the enteroblast on the right, but localises around the internal PAC in the enteroblast on the left (green arrowhead). (F) A meshR2 mutant enteroblast stained for α-spectrin (greyscale) and Rab11 (red), which localises apically (green arrow). The α-spectrin staining reveals that a space has formed between the apical side of the integrating enteroblast and the neighbouring enterocytes. (G) A meshR2 mutant enteroblast stained for α-spectrin (greyscale) and Rab11 (red) that has formed an internal PAC. Rab11 decorates the surface of the internal PAC (green arrowhead). Note the younger, mutant enteroblast on the left (green arrow) localises Rab11 apically. (H) A meshR2 mutant enteroblast (green) with an internal PAC stained for Canoe (red) and α-spectrin (greyscale). Canoe does not localise to the internal PAC, which has no junctions. Scale bars = 5 µm. (I) Diagrams showing the distributions of Canoe, actin and adherens junctions in the three phenotypic classes of meshR2 mutant enteroblasts. The measurement of Canoe’s intensity in the WT and meshR2 mutant enteroblasts is shown in Figure 8—figure supplement 2 D&E. (J) Percentages of mesh, Tsp2a and ssk mutant enteroblasts in each of the classes in (I) compared to a wild-type control (FRT82B clones) based on actin in mutant cells (representative images in Figure 8—figure supplement 1E and F).