Figure 2.
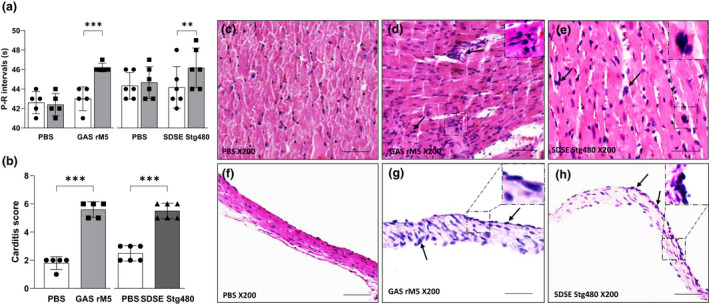
Electrocardiographic and histological changes demonstrate functional impairment and inflammatory changes in the cardiac tissue of rats exposed to streptococcal recombinant proteins. (a) Prolongation of P–R intervals was observed in rats injected with streptococcal recombinant proteins compared with controls rats. (b) Carditis scores were significantly higher in rats injected with GAS rM5 (closed squares) and SDSE Stg480 (closed triangles) than control rats (closed circles). Characteristic mononuclear cell infiltrations (arrows) were observed in the (d, e) myocardium and (g, h) valvular tissues of rats injected with GAS rM5 and SDSE Stg480 compared with (c, f) rats injected with PBS. Data are from one of two experiments with age‐matched rats injected with GAS rM5 (n = 5) and SDSE Stg480 (n = 6). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, by one‐way ANOVA and the Mann–Whitney U‐test. Bars = 50 μm. GAS, group A streptococcus; PBS, phosphate‐buffered saline; SDSE, Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
