Figure 5.
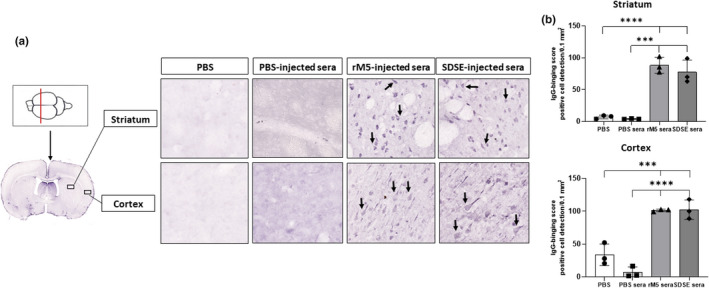
Serum IgG from rats injected with streptococcal recombinant proteins binds to neuronal tissue. Representative images of the striatum and cortex demonstrate binding of serum IgG from rats injected with streptococcal recombinant proteins. Significantly higher serum IgG binding was observed in the striatum and cortex incubated with serum from rats injected with GAS rM5 and SDSE Stg480 than that from rats with PBS. (a) Arrows show IgG binding. (b) IgG‐binding scores were significantly higher in serum from Lewis rats injected with GAS rM5 (closed triangles) and SDSE stg480 (closed diamonds) than from control rats with PBS (closed squares) and PBS (closed circles). Mean number of positive cells in three different sections of the striatum and cortex were detected in 0.1 mm2 at 20× magnification. Data are from one of the two experiments with age‐matched rats injected with GAS rM5 (n = 5) and SDSE Stg480 (n = 6). ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 by one‐way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc multiple comparison test. GAS, group A streptococcus; Ig, immunoglobulin; PBS, phosphate‐buffered saline; SDSE, Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
