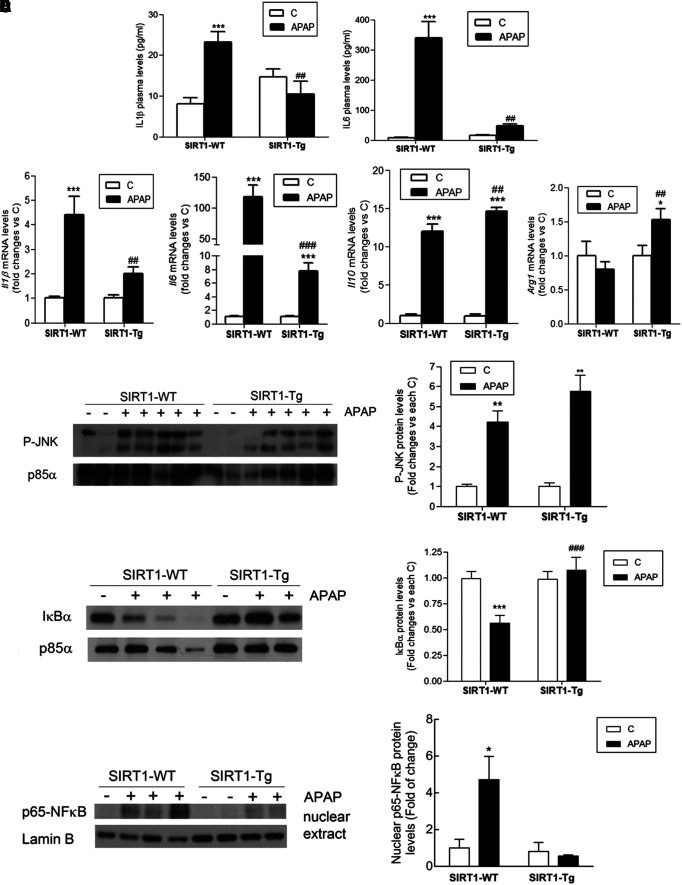
FIG. 5.
SIRT1-Tg mice were protected against the elevation of circulating and hepatic proinflammatory cytokines and NFκB signaling pathway in APAP toxicity. Overnight fasted SIRT1-WT and SIRT1-Tg mice were i.p. injected physiological saline (vehicle) or 300 mg/kg APAP and sacrificed as indicated. (A) Plasma levels of IL6 and IL1β analyzed 6 h after APAP injection. Values are mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. ***p < 0.001 versus control (vehicle) condition. ##p < 0.01 versus SIRT1-WT mice. n = 6–8 mice per group. (B) Il1b, Il6, IL10, and Arg1 mRNA levels determined by qRT-PCR 3 and 6 h after APAP injection. Values are mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 versus control (vehicle) condition. ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 versus SIRT1-WT mice. n = 6–8 mice per group. (C, D, E) Representative immunoblots showing (C) phospho-JNK, (D) IjBa, and (C, D) p85a-PI3K as a loading control and (E) nuclear p65-NFjB and Lamin B as a loading control. After quantification of all blots, results are expressed as fold change relative to control (vehicle) condition and are mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus control (vehicle) condition. ###p < 0.001 versus SIRT1-WT mice. n = 5–6 mice per group. IκBα, inhibitor of kappa B alpha; IL, interleukin; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; mRNA, messenger RNA; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa B; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time PCR.