FIGURE 4.
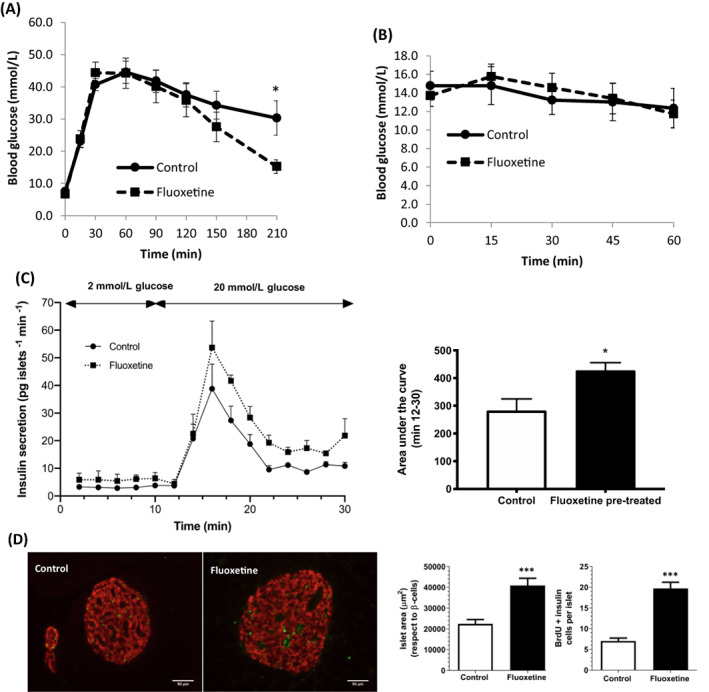
Effects of intermittent intraperitoneal administration of fluoxetine to ob/ob mice. Fluoxetine (10 mg/kg) or vehicle (DMSO) was administered intraperitoneally four times over the course of 14 days to 29‐week‐old ob/ob mice, then mice were subjected to intraperitoneal glucose (A, n = 5, *P < 0.05 vs. control) and insulin (B) tolerance tests after a single administration of glucose (2 g/kg body weight) or insulin (0.75 U/kg body weight) in the presence of fluoxetine or DMSO. Islets isolated from fluoxetine‐ and DMSO‐treated mice were perifused at 0.5 mL/min with a physiological salt solution containing 2 mmol/L glucose (0‐10 min) and 20 mmol/L glucose (10‐30 min). Insulin secretion from perifused islets was measured by radioimmunoassay (C, left panel, n = 3) and areas under the curve were calculated from the perifusion data (C, right panel, n = 3, *P < 0.05 vs. control). Wax‐embedded sections of pancreas from fluoxetine‐ and DMSO‐treated mice were immunostained with antibodies directed against 5‐bromo‐2′‐deoxyuridine (BrdU; green) and insulin (red; D, left panel, scale bars: 50 μm). Islet area and the number of BrdU‐positive beta cells per islet were quantified by analysis of multiple acquisitions of n = 99‐115 islets (D, right panel, ***P < 0.001 vs. control)
