FIGURE 7.
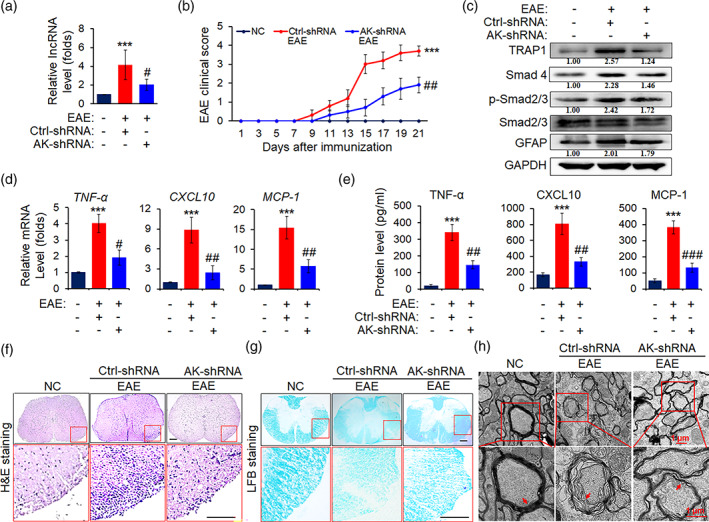
AK018453 knockdown lessens the pathology of EAE mice. On day 7 after administration with recombinant lentivirus carrying GFAP promoter and AK‐shRNA or ctrl‐shRNA sequence, respectively, mice were immunized with or without MOG35–55 for 21 days. (a) The level of lncRNA AK018453 was determined by real‐time PCR assay. ***p < .001 versus NC group; # p < .05 versus ctrl‐shRNA group (n = 10 mice/group). (b) The clinical scores for EAE mice infected with AK‐shRNA or ctrl‐shRNA (n = 10 mice per group). ***p < .001 versus NC group; ## p < .01 versus ctrl‐shRNA group. (c) Western blot assay was used to determine the protein levels of TRAP1, Smad4, p‐Smad2/3, Smad2/3, and GFAP in the spinal cords. (d and e) The production of TNF‐α, CXCL10, and MCP‐1 in the spinal cords and peripheral blood from the AK‐shRNA and ctrl‐shRNA mice was measured by real‐time PCR assay and ELISA assay, respectively. The data are represented as mean ± SEM. ***p < .001 versus NC group; # p < .05, ## p < .01, and ### p < .001 versus ctrl‐shRNA group (n = 10 mice/group). (f) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining was designed to observe the infiltrations of inflammatory cells in spinal cords (scale bars, 50 μm). (g) Luxol fast blue (LFB) staining was utilized to test the medullary sheath damages from spinal cords (scale bars, 50 μm). Red box areas in the upper rows are presented enlarged underneath. (h) Electron microscope (EM) was employed to investigate the severe disruption or mild loosening of the medullary sheath in spinal cords. Red arrow shows the changes of the medullary sheath. Scale bars, 1 μm
