Figure 1.
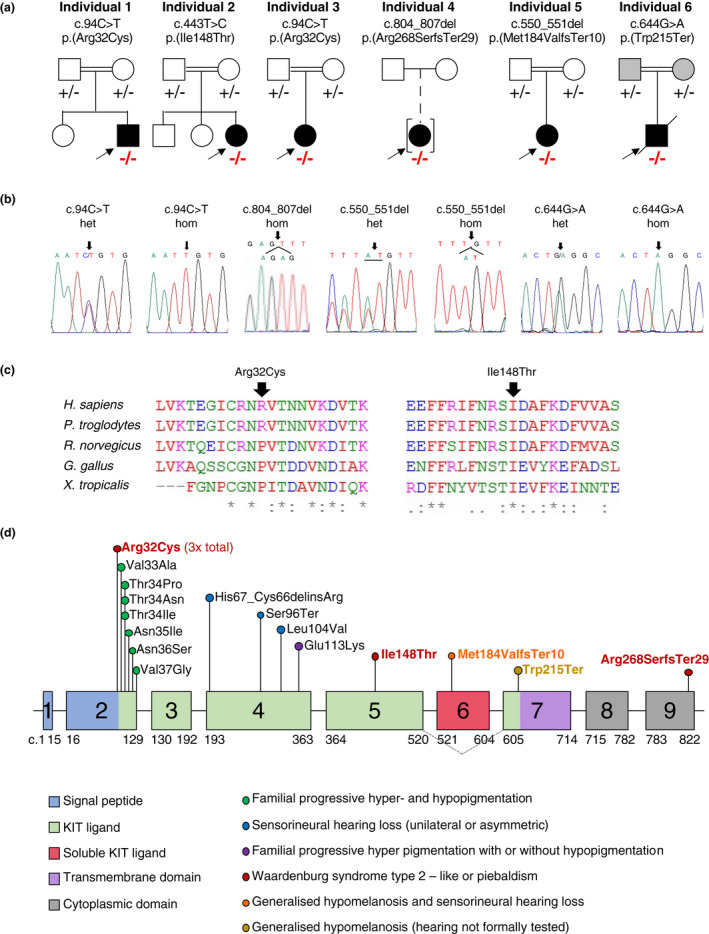
Molecular findings of individuals in our cohort. (a) Pedigree and segregation results (− represents the variant; homozygous variants are marked in red) for the six families with biallelic KITLG variants. (b) Available Sanger electropherograms showing heterozygous (het) or homozygous (hom) variants. (c) Interspecies alignment shows conservation of amino acids involved in non‐synonymous substitutions. (d) Schematic representation of the KITLG gene (NM_000889.4) with c. position, protein domains and features marked. An alternatively spliced isoform skips exon 6 and is represented with grey dotted lines (NM_003994.5). The phenotype of the KITLG variants is shown with coloured circles. The variants we describe are marked in red (WS), orange (generalized hypomelanosis and sensorineural hearing loss) or gold (generalized hypomelanosis with hearing not formally tested). [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
