Figure 2.
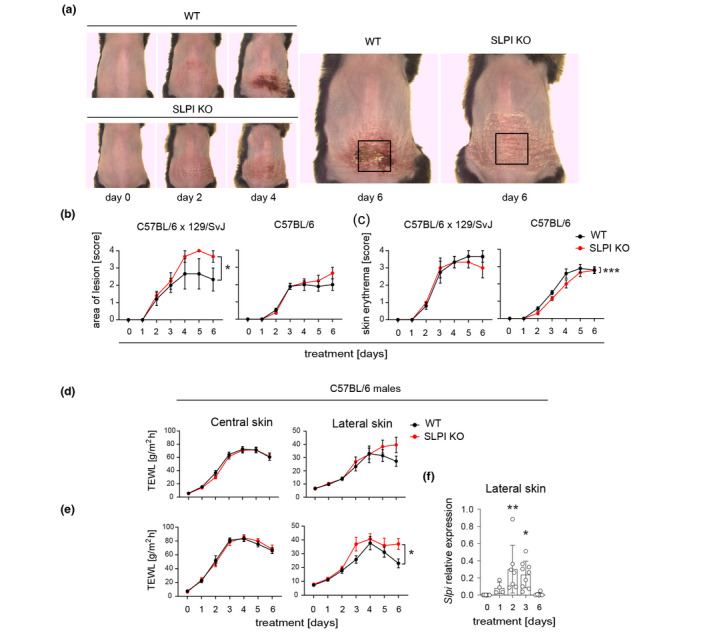
Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor affects size of skin lesions and skin barrier function beyond the IMQ‐challenged site. The mice indicated were subjected to IMQ‐treatment followed by kinetic assessment of the lesion size and skin erythema. (a) The representative image of female WT and SLPI KO mice from mixed background C57BL/6 × 129/SvJ is shown with the indicated site of treatment. (b) Cumulative data (the mean ± SEM) showing size of lesion. n = 3–10 mice in each group. (c) Cumulative data (the mean ± SEM) showing skin erythema. (d) WT and SLPI KO C57BL6 males were subjected to IMQ‐treatment followed by TEWL measurement at the days indicated at the central and lateral skin. The mean ± SEM is shown. n = at least 10 mice in each group. (e) WT and SLPI KO C57BL6 males were injected with 0.9% NaCl i.d. at the stimulated site prior to IMQ‐treatment. TEWL was then measured at the days indicated at the central and lateral skin. The mean ± SEM is shown. n = at least 7 mice in each group. (f) The lateral skin of WT mice was harvested at the days indicated and subjected to qPCR analysis for Slpi mRNA levels. The data are shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Dots indicate individual mice. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; by ANCOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test.
