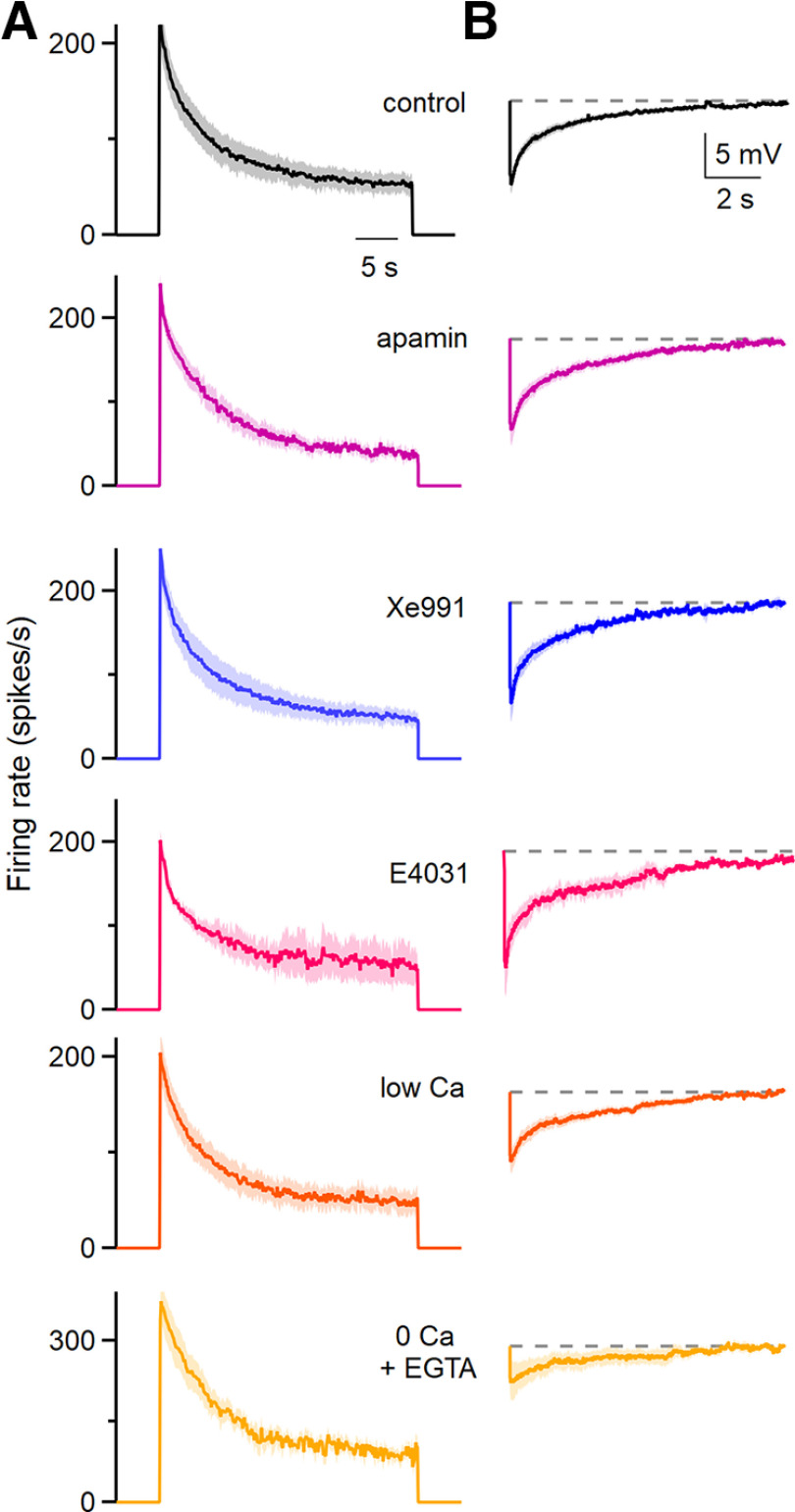
Figure 3.
The pharmacological sensitivity and calcium dependence of spike frequency adaptation and the subsequent afterhyperpolarization. A, Average instantaneous firing frequencies evoked by 200 pA depolarizing currents for 30 s in the indicated conditions. The effects of apamin (300 nm; a blocker of SK Ca2+-activated K channels), XE-991 [10 μm; an antagonist of Kv7 channels (KCNQ, M-current)], and E4031 [a blocker of KCNH1 (ERG K channels)] were assessed. Low Ca solution consisted of 0.1 mm external Ca2+ and 4 mm external Mg2+, 0 Ca2+ solution consisted of 0 Ca2+ and 1 mm EGTA. Control, n = 18 cells (9 animals); apamin, n = 7 cells (four animals); XE991, n = 5 cells (three animals); low Ca, n = 10 cells (7 animals); 0 Ca + EGTA, n = 7 cells (6 animals). Shading indicates the SE. B, The average AHPs following the current steps in A are shown for the indicated conditions. Shading indicates the SE.