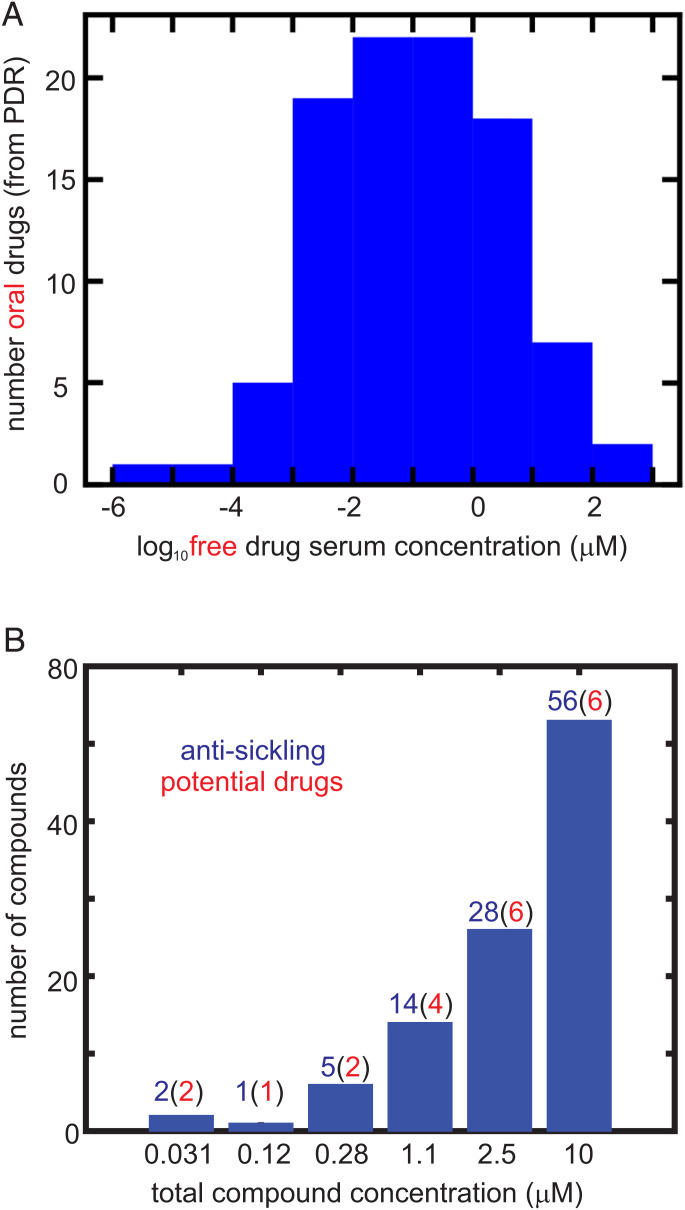
Fig. 5.
Comparing inhibitory concentrations in assay and oral drug concentrations in the PDR. (A) Distribution of 97 free oral drug concentrations (Cmax) in the 2015 version of the PDR. The free concentration was given either explicitly in the PDR or was obtained from the given total serum Cmax and the percentage bound to serum proteins. (B) Distribution of ReFRAME total compound concentrations with statistically significant inhibition at each concentration, defined as . The red numbers in parentheses result from multiplying the number (in blue) of compounds by the fraction of oral drugs with that free concentration or higher from the distribution in Fig. 5A. In the 2,000-fold diluted blood used for the assay, the Hb molecule is at a concentration of ∼1 μM, while the molar concentration of red cells is ∼4 fmol. Consequently, for inhibitory mechanisms other than those resulting from binding to Hb, the total compound concentration in the assay is also the free concentration. For compounds that inhibit by binding to Hb, the free concentration is less than the total concentration.