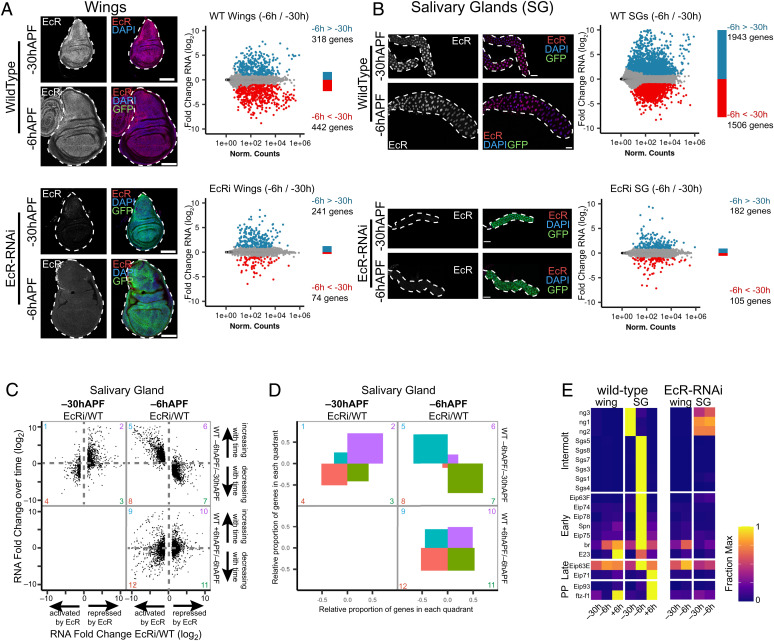
Fig. 2.
EcR is required to promote genome-wide changes in gene expression over time. (A and B) Left: Confocal images of wild-type and EcR-RNAi wings (A) and salivary glands (B) at −30hAPF and −6hAPF stained with anti-EcR (red) and DAPI (blue). GFP (green) indicates expression of the GAL4 driving RNAi expression. (Scale bars: 100 μm.) Right: MA plots of RNA-seq data comparing wild-type (Top) or EcR-RNAi (Bottom) tissues between −30hAPF and −6hAPF. Differentially expressed genes (Padj < 0.05; absolute log2 fold change >1) are colored red and blue. (C) Scatterplots of RNA-seq values for differentially expressed genes in EcR-RNAi salivary glands. The ratio between EcR-RNAi and wild-type is shown on the x-axis for −30hAPF and −6hAPF. The ratio between adjacent wild-type stages is shown on the y axis. (D) Plots indicating the proportion of genes located in each quadrant for the three scatterplots shown in (C). (E) Heatmap of RNA-seq values (fraction of max) from wild-type and EcR-RNAi tissues for select genes that exhibit ecdysone-dependent puffs in salivary glands. PP indicates prepupal.