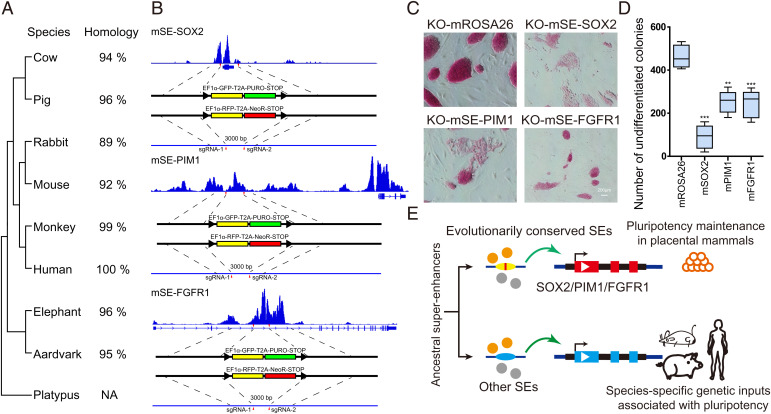
Fig. 6.
The three conserved SEs are essential for pluripotency. (A) The evolutionary tree of the three SE conserved subregions among nine representative mammals. Their sequence identities to humans are listed on the right. (B) The strategy to disrupt the three conserved SEs in murine PSCs by CRISPR-Cas9. (C) AP staining assay of murine PSCs with SE disruption. Murine PSCs lost their pluripotency when the three conserved SEs were destroyed. The editing of the murine ROSA26 locus was used as the control. Scale bar, 200 µm. (D) Numbers of undifferentiated AP-positive colonies under different editing treatments. n = 5 independent experiments (**P <0 0.01, ***P < 0.001). (E) The model of ancestral SE evolution in mammalian pluripotency maintenance. We propose that evolutionarily conserved SEs are critical in maintaining mammalian pluripotency, and other SEs may contribute to the species-specific genetic inputs associated with pluripotency. m, mouse. NA, not available. PURO, puromycin resistant. NeoR, neomycin resistant.