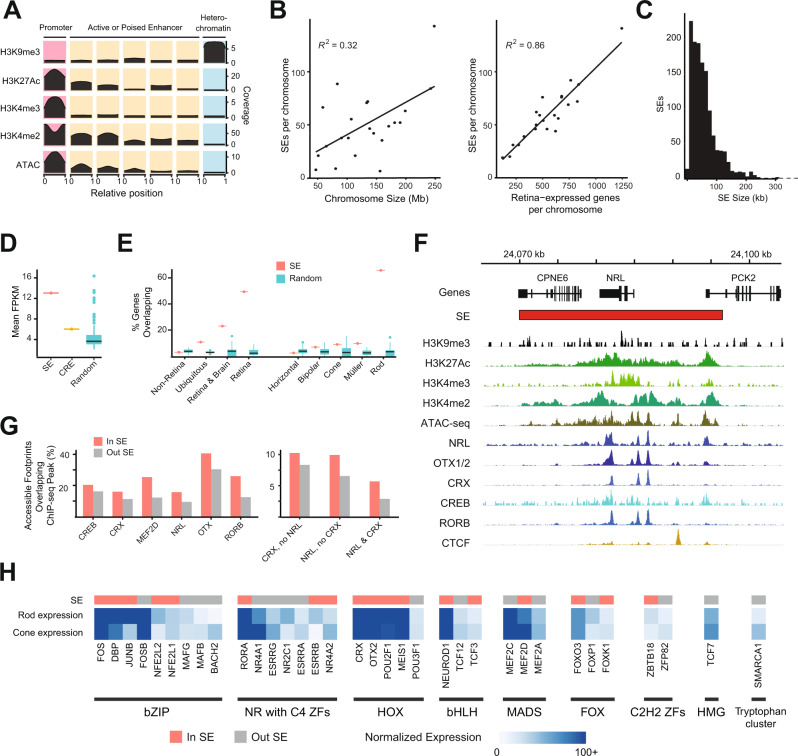
Fig. 3. Retinal SE identification and characterization.
A Chromatin states identified from histone marks and ATAC-seq data (low signal states not shown, see Fig. S3). Plots in each cell indicate the mean coverage for each mark across the genomic regions aligned and resized to a 0 to 1 scale, e.g., regions assigned the heterochromatin state contain uniformly high H3K9me3 coverage across the entire region and low coverage of all other marks. B Number of SE per chromosome versus chromosome size (left) and versus number of retina-expressed genes (right). Correlation is measured as Pearson’s r2. C Size distribution of SEs in retina. D Mean expression of genes with transcription start sites (TSS) in SE (n = 1), CRE (n = 1), and random SE-sized genomic regions (n = 100). Boxplots represent the median and interquartile range (IQR); whiskers mark 1.5x the IQR; data beyond 1.5x the IQR are plotted as individual points. E Percentage of genes in various enrichment groups (see methods) with at least one TSS located in a SE (n = 1) or random SE-sized region (n = 100). Boxplots represent the median and interquartile range (IQR); whiskers mark 1.5x the IQR; data beyond 1.5x the IQR are plotted as individual points. [F] SEs, histone marks, chromatin accessibility, and TF residency for the NRL locus. G Percentage of accessible genomic footprints (defined via ATAC-seq) inside and outside of SEs which contain ChIP-seq narrow peaks for the indicated TF(s). H Selection of TF motifs enriched in SE-overlapping accessible genomic footprints containing NRL and CRX relative to accessible footprints without NRL or CRX. The bar on top indicates whether the gene coding for the TF is overlapping a SE (red) or not (grey). The heatmap shows normalized gene expression in rods and cones from the Human Protein Atlas. TF families as defined by TFClass are indicated along the bottom edge. Abbreviations ATAC-seq Assay for transposase-accessible chromatin sequencing, SE Super-enhancer, FPKM Fragments per kilobase million, TSS Transcription start site, ChIP-seq Chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing, C2H2 ZFs C2H2 zinc finger factors, bZIP Basic leucine zipper factors, NR with C4 ZFs Nuclear receptors with C4 zinc fingers, HOX Homeodomain factors, bHLH Basic helix-loop-helix factors, MADS MADS-box factors, HMG High-mobility group domain factors, FOX Fork head/winged helix factors, RHR Rel homology region factors.