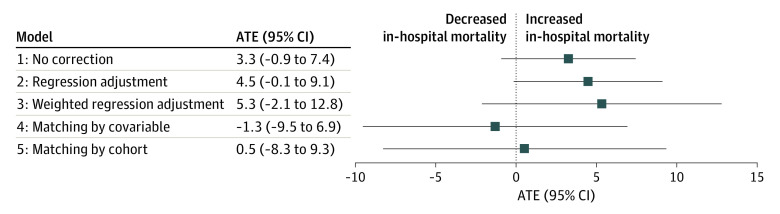
Figure 3. Average Treatment Effect (ATE) Estimation of Association of Norepinephrine With In-Hospital Mortality.
Model 1: ATE estimation in the combined US and French cohort with no correction. Model 2: ATE estimation in the combined US and French cohort through regression adjustment. Model 3: weighted regression adjustment for all untreated patients and US patients weighted according to their similarity with untreated French patients. Model 4: ATE estimation in the US cohort matching each US patient with a treated French patient with similar baseline confounders combined with ATE estimate in the French cohort to generate a global ATE in the combined cohorts (US and French). Strategy 5: ATE estimate in the US cohort matching each US patient with a treated French patient with a similar probability of belonging to the US cohort given confounders combined with ATE estimate in the French cohort to generate a global ATE in the combined US and French cohorts. Models used the doubly robust approach and multivariate imputation by chained equations.