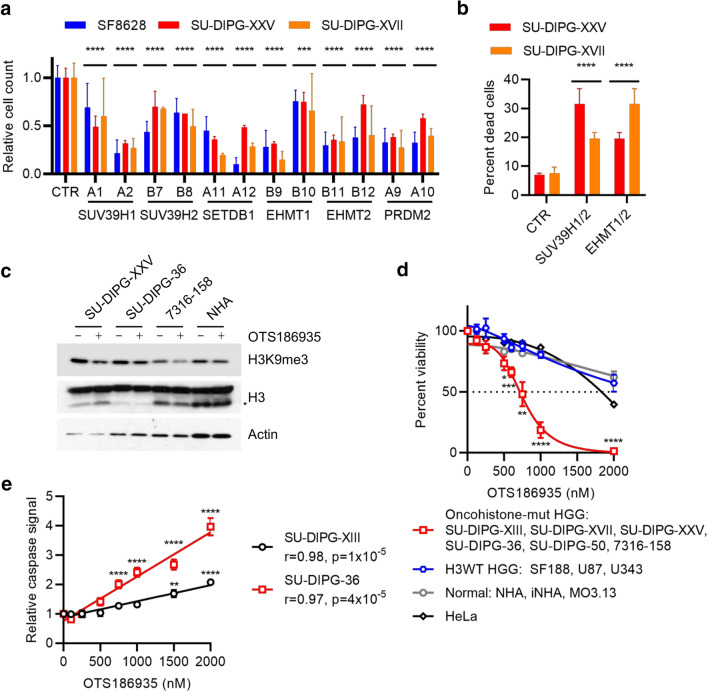
Fig. 6.
Oncohistone-mutant pHGG cells are vulnerable to inhibition of H3K9 methylation. A Viable cell counts of H3.3K27M-mutant cell lines transduced with shRNA lentiviral constructs targeting H3K9 methylases, expressed relative to cells transduced with control shRNA. Two separate shRNA clones were used for each gene. Results show mean ± standard deviation of 2–5 biological replicates. p: ANOVA comparing each clone to control shRNA (CTR). ****p < 0.0001. B Percent cell death of H3.3K27M-mutant cell lines transduced with combinations of control shRNA targeting H3K9 methylases. Results show mean ± standard deviation of 3 biological replicates. p: ANOVA comparing each clone to control shRNA (CTR). ****p < 0.0001. C Cells treated with DMSO or OTS186935 (1,500 nM) for 4 days were analyzed by western blotting. *: clipped H3. D Relative viable cell counts of cell lines treated for 4 days with DMSO or increasing doses of OTS186935. Results show mean ± standard error for groups of cell lines. Each cell line was analyzed in six biological replicates. E Quantification of caspase activation assay in SU-DIPG-XIII and SU-DIPG-36 cells treated with DMSO or increasing doses of OTS186935 and measured after 24 h. Results show mean ± standard error of 6 biological replicates, with 2 fields of view measured per replicate. **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001; r: Pearson correlation. p values for overall correlation were determined with a t test and for comparisons to DMSO by ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test