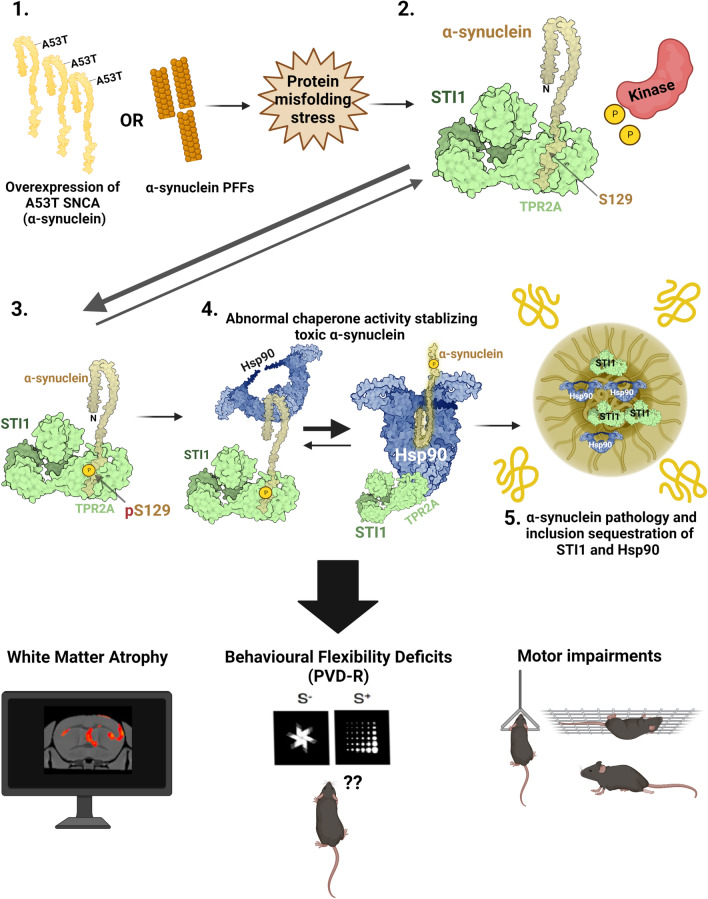
Fig. 7.
Hypothetical model of STI1 regulation of toxic α-synuclein and promotion of phosphorylation at S129. 1 Toxic α-synuclein species disturb chaperome and contribute to protein misfolding stress. 2 The TPR2A domain of STI1 interacts with the C-terminal domain of α-synuclein forming a complex in the brain. 3 The STI1-α-synuclein interaction may facilitate α-synuclein phosphorylation at S129. 4 STI1 may scaffold α-synuclein to deliver it to Hsp90. 5 STI1 and Hsp90 are sequestered into inclusions in multiple brain regions. Thus, α-synuclein function and potential to aggregate may depend on different chaperones and their co-chaperones in specific cell types. These toxic effects lead to white matter atrophy, cognitive, and motor deficits. Figure designed with BioRender.com software