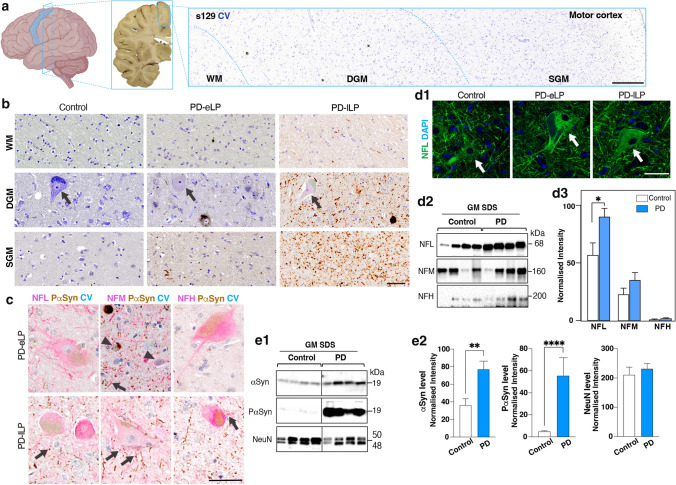
Fig. 4.
Lewy pathology and neurofilament proteins in the motor cortex in motor PD. a Anatomical location of post-mortem primary motor cortex (blue contour) with tissue sampled for pathological studies taken from the medial aspect of the superior surface. The sampled tissue was usually dissected in the coronal slice containing the mammillary body. SGM, DGM, and WM are shown from a formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded section of a representative PD case labelled with s129 (against phospho-Ser129 α-synuclein, brown) and counterstained with cresyl violet (CV, blue); the scale bar represents 200 mm. b Regional Lewy pathological load (s129, brown) in SGM, DGM, and WM of representative PD cases compared to a pathologically spared control. Arrows indicate Betz cells; the scale bars represent 50 mm for b, c, and d. c Lewy pathology (PaSyn, brown) was mainly found in small neurons (arrowheads, blue CV). In large Betz cells (NFL, pink), Lewy pathology was more dominant in their processes (arrows, PaSyn, brown). d1 Representative immunofluorescent confocal images of neurofilament light chain (NFL) expressing neurons in control and PD motor cortices. d2 Representative western immunoblots (SDS-fraction) of neurofilament proteins in the motor cortex of motor PD (n = 12) and controls (n = 8). d3) Column graphs of the mean ± SEM normalised neurofilament levels in motor cortex. Mann–Whitney test covarying for gender. *p < 0.05. e1 Representative western immunoblots of pan αSyn (BD-1), phosphorylated αSyn (s129; PαSyn), and NeuN detected in motor cortex (n = 8, 12 for controls and PDs, respectively). e2) Column graphs were presented as mean ± SEM. Mann–Whitney tests; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001. DGM deep cortical grey matter, GM grey matter, PD-eLP PD cases with early Lewy pathology (Braak stage 4), PD-lLP PD cases with late Lewy pathology (Braak stage 6), SGM superficial cortical grey matter, WM subcortical white matter. Scale bars are 50 mm for all images unless indicated