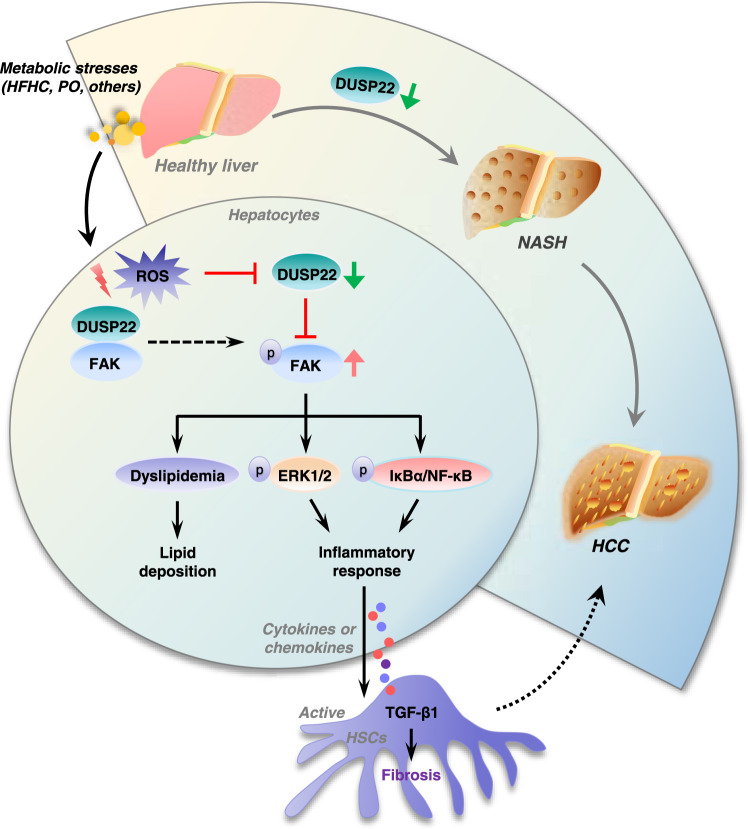
Fig. 9. Schematic diagram showing the mechanism of action of DUSP22 in NASH-HCC.
Excessive metabolic stimuli, such as HFHC and PO, promotes ROS generation, which leads to DUSP22 downregulation, thereafter contributing to the activation of FAK signaling through phosphorylating FAK at Y397 and Y576 + Y577 residues. FAK activation results in lipid deposition and inflammatory response via activating ERK1/2 and NF-κB signaling pathways. Inflammatory factors released from hepatocytes facilitates hepatic fibrosis. All these effects mediated by DUSP22/FAK axis contribute to the progression of NASH and NASH-associated HCC.