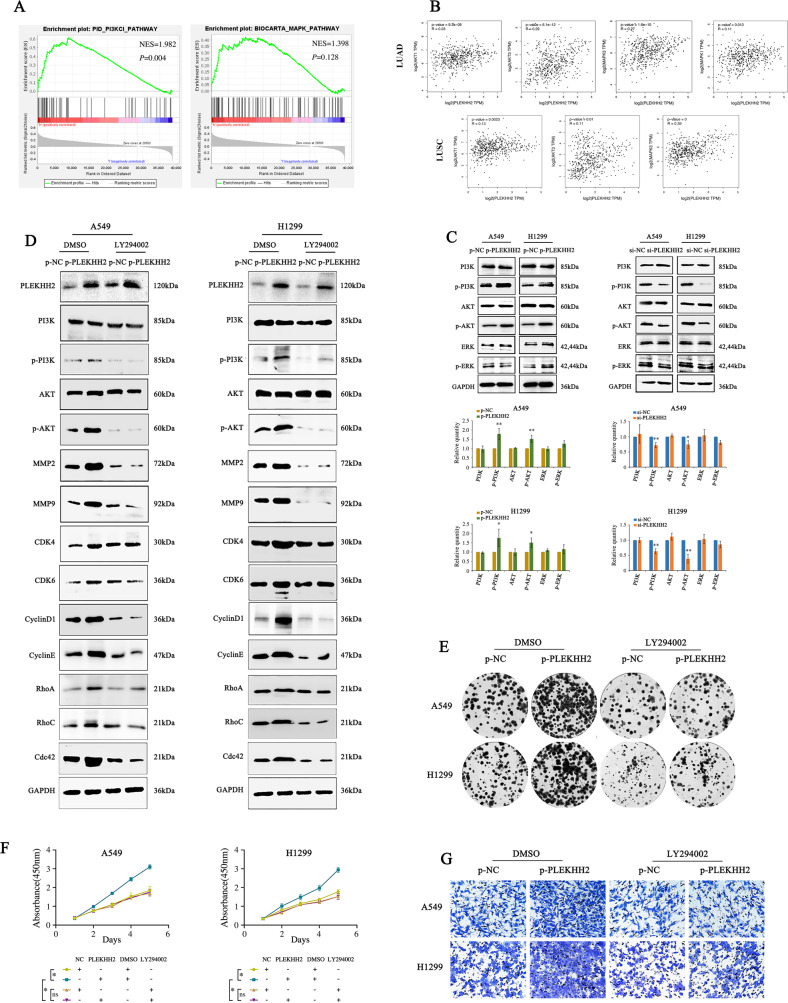
Fig. 4. PLEKHH2 promotes the malignant phenotype of lung cancer cells by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
A GSEA analysis showed that, in lung adenocarcinoma, the expression of PLEKHH2 enriched in PI3K regulator activity in the TCGA cohort. B GEPIA analysis showed that PLEKHH2 was positively correlated with AKT and MAPK in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC). C The upregulation of PLEKHH2 significantly increased p-PI3K and p-AKT levels. The p-ERK level was not significantly upregulated, and the expression of total PI3K, AKT, and ERK did not change. In the cells with downregulated PLEKHH2 expression, p-PI3K and p-AKT levels were decreased, but p-ERK did not show a significant reduction. There was no significant change in total PI3K, AKT, and ERK proteins. D After inhibiting the PI3K signaling pathway via LY294002 treatment, an upregulation in PLEKHH2 expression did not significantly increase p-PI3K, p-AKT, and proliferation- and invasion-related proteins, as evidenced via western blotting. Statistical analysis in lung cancer cell lines is shown in Supplementary Fig. 4A and B. Results of the clone formation assay (E, Statistical analysis is shown in Supplementary Fig. 4C and D), CCK-8 assay (F), and Matrigel Transwell assay (G, Statistical analysis is shown in Supplementary Fig. 4E and F) showed that the upregulation PLEKHH2 expression had no significant effect on cell proliferation and invasion ability after treatment with LY294002. P < 0.05 indicates statistical significance, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.