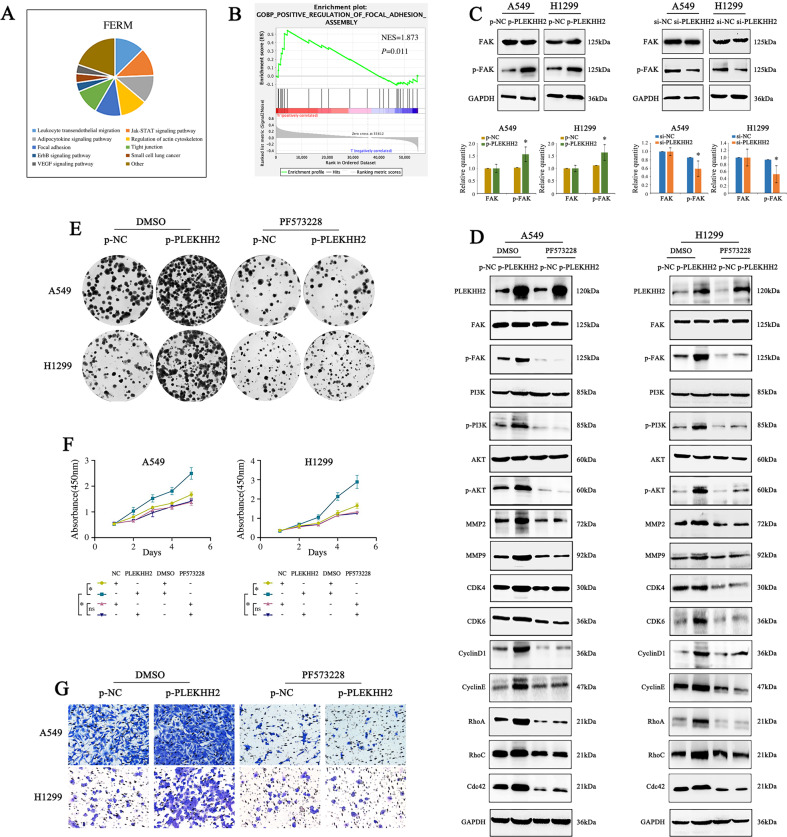
Fig. 5. PLEKHH2 activates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by promoting FAK phosphorylation.
A The SMART database was used to analyze the cellular functions of proteins containing the FERM domain. B The GSEA database predicted that PLEKHH2 was enriched in focal adhesion assemblies. C Overexpression of PLEKHH2 promotes FAK phosphorylation, which plays an important role in the focal adhesion assembly process. PLEKHH2 knockdown decreased FAK phosphorylation, but the total protein level of FAK did not change significantly. D After inhibiting the activity of the FAK via PF573228 treatment in A549 and H1299 cells, an increase in PLEKHH2 expression did not increase p-PI3K, p-AKT, or other proliferation-, migration-, and invasion-related proteins. Statistical analysis is shown in Supplementary Fig. 5A and 5B. Results of the clone formation assay (E, Statistical analysis is shown in Supplementary Fig. 5C and D), CCK-8 assay (F), and Matrigel Transwell assay (G, Statistical analysis is shown in Supplementary Fig. 5E and F) showed that, following the inhibition of FAK phosphorylation, the upregulation of PLEKHH2 did not significantly promote cell proliferation and invasion ability. P < 0.05 indicates statistical significance, *P < 0.05.