Fig. 2. LYSET is required for global lysosomal enzyme transport via M6P-tagging.
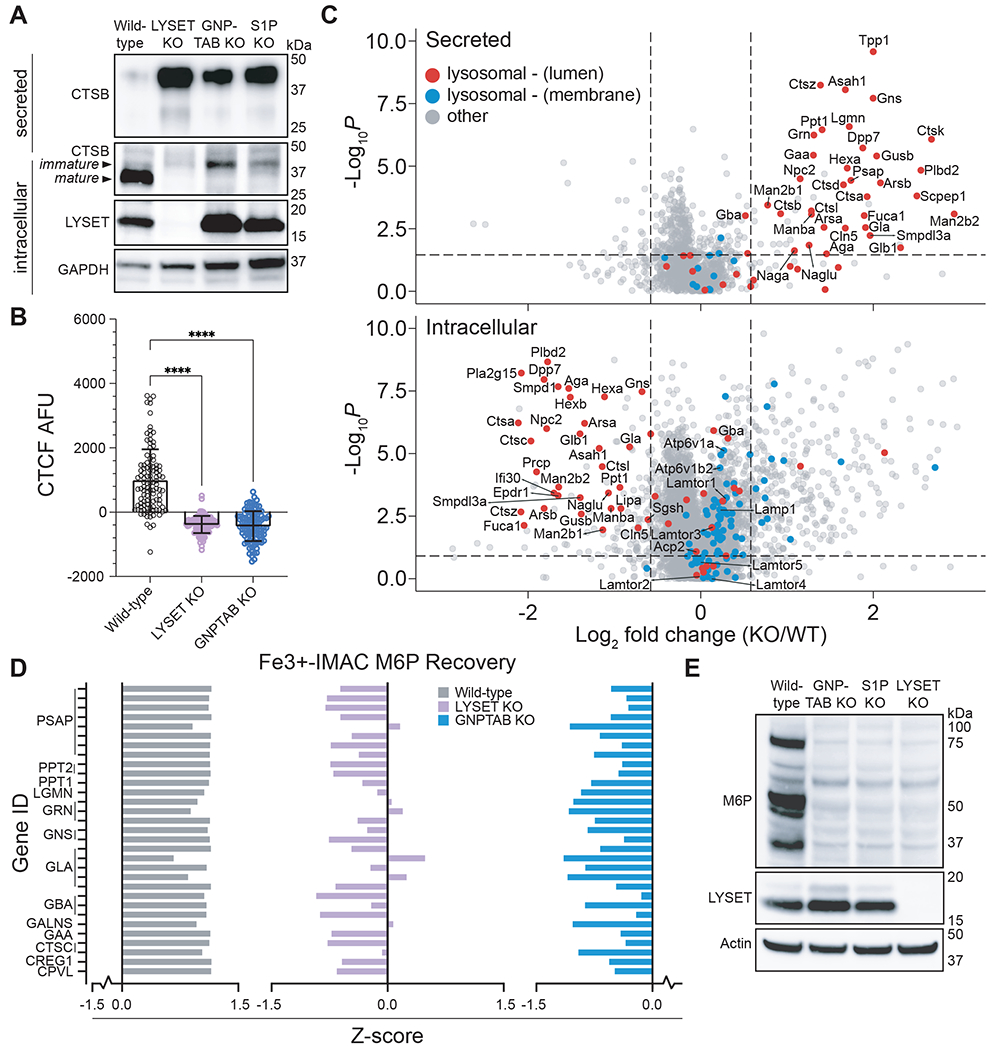
(A) Immunoblot analysis of cathepsin B (CTSB) in lysates (intracellular) and in extracellular medium (secreted) from wild-type cells and clonal 293FT cell lines containing knockout (KO) mutations in indicated genes. (B) Cathepsin activity in cells was determined by quantification of BMV-109 fluorescence signal in live 293FT wild-type and KO cells as the raw corrected total cellular fluorescence (CTCF) in arbitrary fluorescence units (AFU) (mean ± SD, n = 100 cells, **** p<0.0001; significance determined via one-way ANOVA with a post-hoc Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). (C) Proteomic analysis of wild-type and LYSET KO MEFs by unbiased data independent acquisition (DIA). DIA was used for intracellular and secreted proteins. (D) Z-score analysis of individual peptides that contain the M6P moiety as determined using glycoproteomics. Peptides were derived from indicated lysosomal proteins in wild-type, LYSET KO and GNPTAB KO 293FT cells; n = 3 replicates for each cell line. (E) Immunoblot analysis of M6P-tagged proteins from 293FT wild-type, GNPTAB KO, S1P KO, and LYSET KO cells using an M6P-specific single-chain antibody fragment (M6P).
