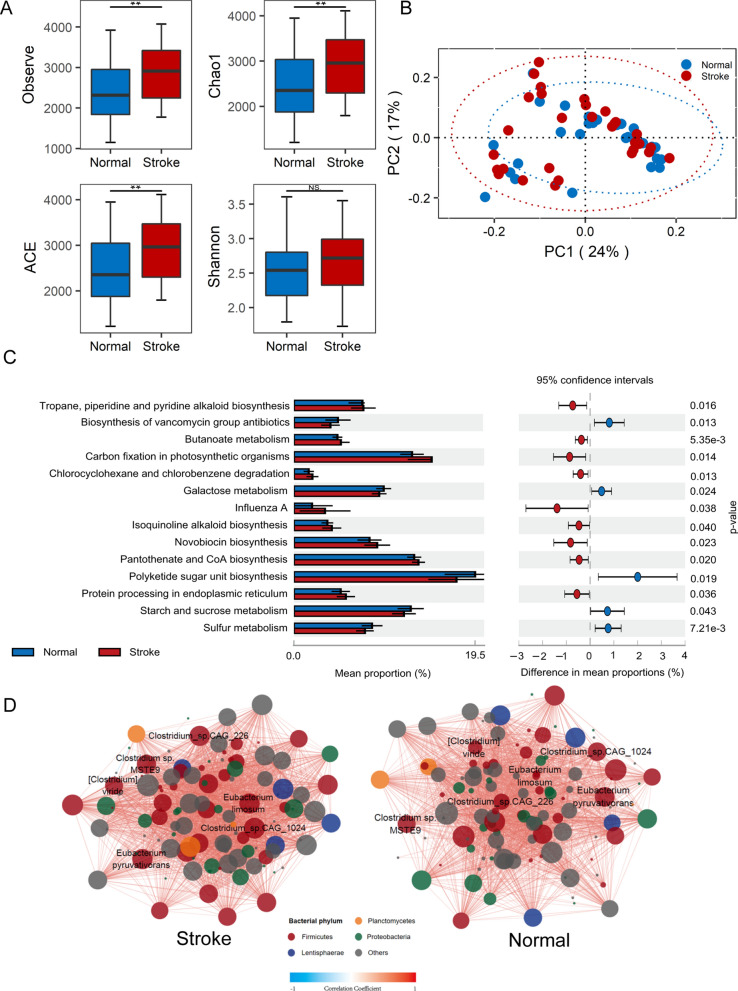
Fig. 5.
Gut microbiota taxonomic and functional comparison between CIS and the controls. A depicts the indices of alpha-diversity. B depicts the Principal Coordinates Analysis (PCoA) of beta-diversity. Each point represents a single sample in CIS and the controls. The two principal components (PC1 and PC2) explained 24% and 17%. C shows the relative abundance of KEGG pathways of functional annotations in the gut microbiota. The barplot with 95% confidence intervals denote the significantly different KEGG pathways between CIS and controls. D Gut bacterium-bacterium ecological network in CIS versus the controls. Correlations between taxa were calculated through Spearman’s rank correlation analysis. Statistical significance was determined for all pairwise comparisons. Only statistically significant correlations (P < 0.05) with |r|> 0.5 were plotted. The size of node, corresponding to individual microbial species, is proportional to the number of significant inter-species correlations. The color of node indicates the phylum to which the corresponding microbial species belong to. The color intensity of connective lines is proportional to the correlation coefficient, where blue lines indicate inverse correlations and red lines indicate positive correlations