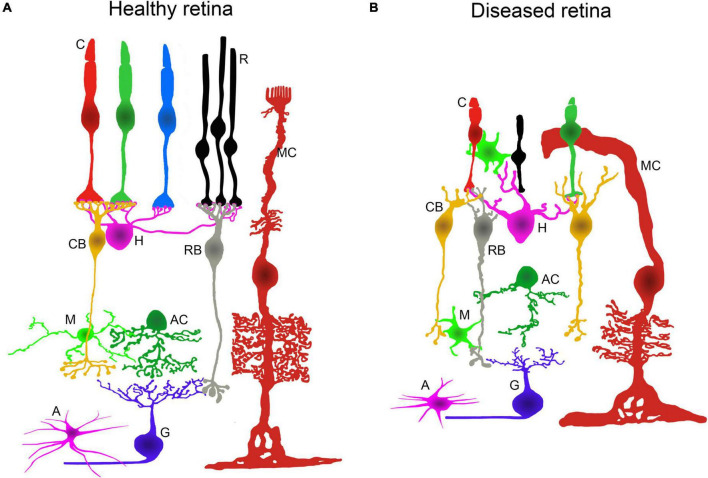
FIGURE 1.
Retinal alterations associated to IRDs. Schematic representation of the retinal neurons and glial cells in healthy and diseased retinas. (A) Normal morphology and layered architecture of the mammalian retina in physiological conditions. (B) During retinal neurodegenerative processes, changes in morphology and connectivity take place. There is a loss of rods and major morphological alterations in cones. The dendrites from horizontal and bipolar cells degenerate. There is a generalized retraction and loss of axons, dendrites, and synaptic connections in the inner retinal neurons. Müller cells, microglia, and astrocytes display an activated state and undergo morphological changes. C: cone photoreceptor; R: rod photoreceptor; MC: Müller cell; CB: cone bipolar cell; H: horizontal cell; RB: rod bipolar cell; M: microglial cell; AC: amacrine cell; A: astrocyte; G: ganglion cell.