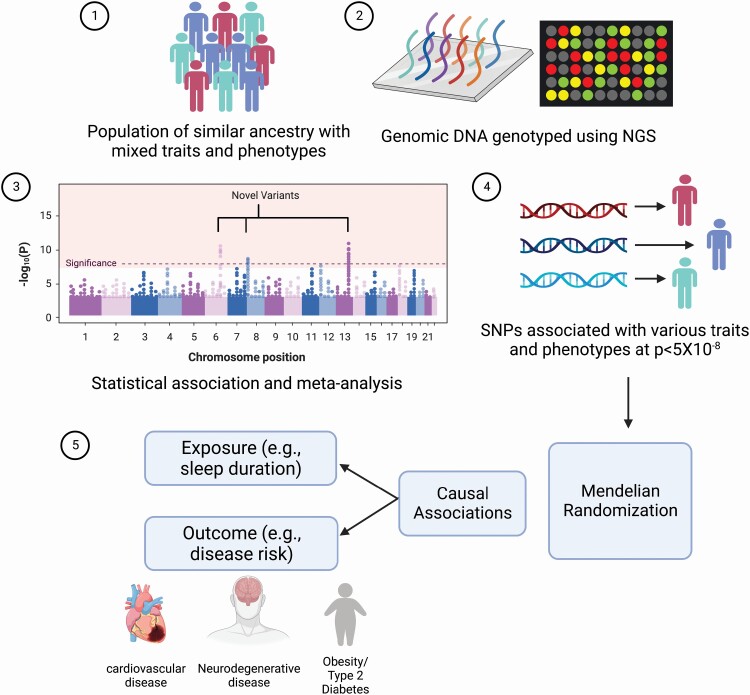
Figure 1.
Overview of identification of causal associations using the Mendelian Randomization approach. 1. Population of similar ancestry but mixed phenotypes are considered for genotyping. 2. All participants are genotyped using different techniques to identify genomic regions likely to be associated with a given phenotype. 3. Statistical association tests and meta-analyses are used to identify novel causal genetic variants (single nucleotide polymorphisms – SNPs). 4. SNPs that pass the rigid thresholds for each trait are considered statistically significant and are utilized as genetic instruments for subsequent analyses. 5. By virtue of their random allocation, such genetic variants are utilized by Mendelian Randomization analyses to identify causal associations between any modifiable exposure (e.g. sleep duration) and outcome (risk for common complex disease).