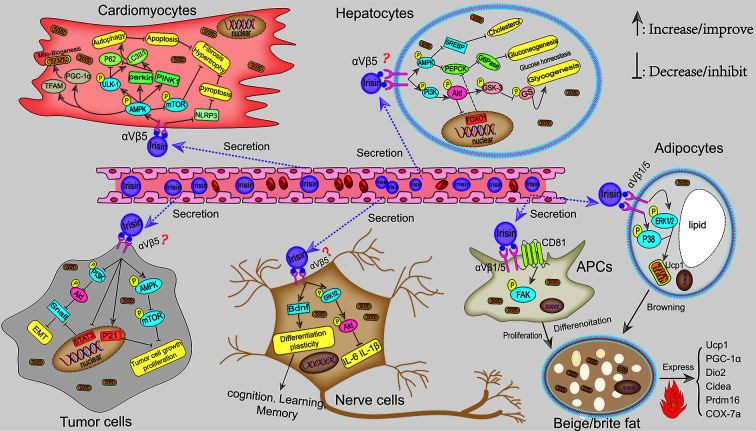
Figure 2.
Potential mechanisms signaling pathways for the actions of irisin in the pathological tissues. Irisin protects against DIO by inducing the recruitment of beige fat to dissipate energy into heat. This mechanism is involved in p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 pathways, as well as FAK-mediated beige APCs proliferation. In addition, irisin attenuated diet-induced metabolic disorders, including NAFLD and hepatic steatosis by promoting the synthesis of liver glycogen via PI3K/Akt/GSK3-GS and inhibiting the generation of liver gluconeogenesis through AMPK-PEPCK/G6Pase and PI3K/Akt/FOXO1-mediated PEPCK/G6Pase pathways. In brain tissues, irisin promoted cognition and neuro development via inhibiting the inflammatory response and activating BDNF-mediated nerve cell survival, differentiation, and plasticity. Moreover, irisin affects the proliferation, migration, and invasion of tumor cells probably by binding integrin αV/β5–mediated PI3K/Akt-Snail-EMT and AMPK-mTOR pathways, which has great therapeutic prospects for inhibiting cancer development. Moreover, exercise-induced irisin can also reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. In cardiomyocytes, irisin stimulated AMPK-mediated autophagy and mitobiogenesis by binding to its receptor integrin αV/β5, thereby relieving cardiac hypertrophy and injury.