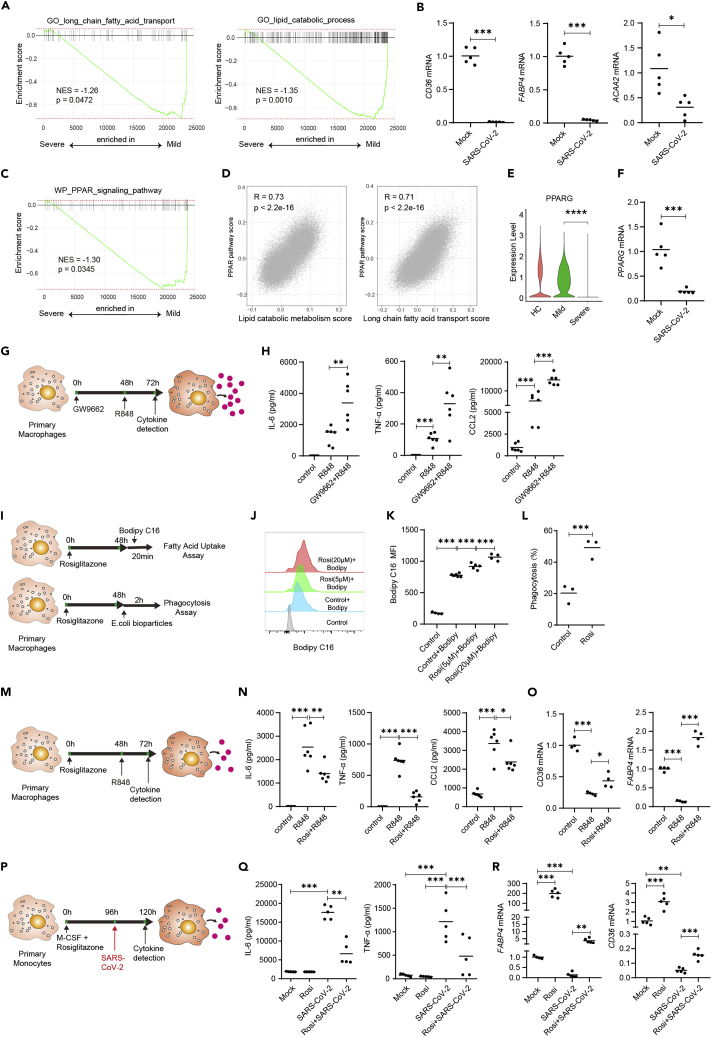
Figure 7.
The PPARγ agonist rosiglitazone reduces hyperinflammation in macrophages stimulated with SARS-CoV-2 or TLR7/8 agonist
(A) GSEA analysis of long-chain fatty acid transport and lipid metabolic process gene sets in macrophages from severe versus mild COVID-19 patients.
(B) Human primary monocyte-derived macrophages were stimulated with SARS-CoV-2 virus (MOI = 0.1) for 24 h. mRNA levels of CD36, FABP4, and ACAA2 were detected by real-time PCR.
(C) GSEA analysis of PPAR signaling pathway in macrophages from severe versus mild COVID-19 patients.
(D) Pearson correlation plot of metabolic scores versus PPAR pathway score in macrophages from BALF of HCs and patients with COVID-19.
(E) Expression levels of PPARG in macrophages from BALF of patients with HC, mild or COVID-19.
(F) Human primary monocyte-derived macrophages were stimulated with SARS-CoV-2 virus (MOI = 0.1) for 24 h. mRNA level of PPARG were detected by real-time PCR. Shown (B&F) are representative data (mock, n = 5; SARS-CoV-2, n = 5) from 3 independent donors with mean values.
(G and H) Human primary macrophages were cultured in the presence of PPARγ inhibitor GW9662 (2μM). At 48 h, the cells were stimulated with R848. IL-6, TNF-α, and CCL2 levels in culture supernatant 24 h after stimulation. Shown are representative data (mock, n = 6; R848, n = 6, Rosi + R848, n = 6) from 3 independent donors with mean values.
(I) Human primary macrophages were cultured in the presence of PPARγ activator rosiglitazone. At 48 h, the cells were incubated in medium containing 0.2μM BODIPY FL C16 for 20 min or in medium containing 0.1mg/mL pHrodo Green E. coli BioParticles Conjugate for 2 h at 37°C.
(J–L) Uptake of fatty acids (J-K) and E. coli bioparticles (L) were compared between groups using flow cytometry. Shown are representative data from 2 independent donors with mean values.
(M and N) Human primary macrophages were cultured in the presence of PPARγ activator rosiglitazone (5μM). At 48 h, the cells were stimulated with R848. IL-6, TNF-α, and CCL2 levels in culture supernatant 24 h after stimulation (N). Shown are representative data (mock, n = 6; R848, n = 6, Rosi + R848, n = 6) from 3 independent donors with mean values.
(O) Human primary macrophages were cultured as in K, CD36 and FABP4 mRNA levels in cells were detected by real-time PCR 24 h after stimulation.
(P–R) Human primary monocytes were differentiated to macrophages with M-CSF (colony stimulating factor 1) for 4 days in the presence of rosiglitazone. The differentiated cells were then stimulated with SARS-CoV-2 (MOI = 0.1) for 24 h (P). IL-6 and TNF-α levels in culture supernatant were detected by ELISA (Q). mRNA levels of CD36 and FABP4 in cells were detected by real-time PCR 24 h after stimulation (R). Shown are representative data (mock, n = 5; Rosi, n = 5, SARS-CoV-2, n = 5, Rosi + SARS-CoV-2, n = 5) from 3 independent donors with mean values. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Unpaired, two-tailed Student’s ttest (for B, F, and L) or one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s post hoc test (for H, K, N, O, Q, and R) were performed to compare between groups.