Fig. 3.
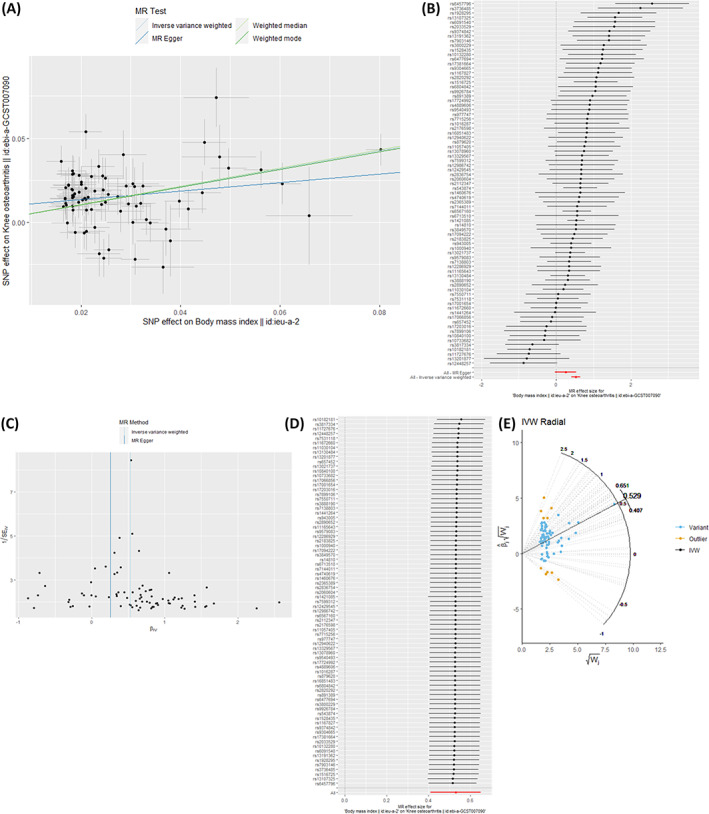
Results commonly presented in Mendelian randomization (MR) studies. (A) A scatterplot is often presented comparing results of the different summary‐level meta‐analyses. Here we are looking for consistency in the slope (ie, causal effect estimate) between the different approaches, which we do observe. The MR‐Egger slope is slightly weaker due to the intercept not being fixed at 0, although the intercept is close to 0 and the slope is similar in direction and magnitude to the other methods, meaning we can be more confident in the inverse‐variance weighted (IVW) causal effect estimate. (B) A single‐nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis can be performed to detect heterogeneity, with each point on the forestplot representing the Wald ratio for an individual SNP. Here we do observe heterogeneity in effect estimates, which means we should be cautious of horizontal pleiotropy, but the majority of SNPs do provide causal effect estimates in the positive direction. (C) The funnel, or volcano, plot shows the Wald ratio for each SNP on the x axis and the weight on the y axis (ie, the inverse of the standard error). Asymmetry in this plot would indicate that an SNP has a large effect on the outcome, relative to its precision, indicating pleiotropy. As this plot is relatively symmetrical, we can be more confident in the IVW estimate. (D) A leave‐one‐out analysis can identify outlier SNPs with a large effect on the overall IVW estimate. If the effect estimate (indicated by the points, with horizontal bars indicating 95% confidence intervals) changes in magnitude and/or direction when an individual SNP is excluded, this is evidence that the SNP is an invalid instrument. In this case, there is no evidence to suggest any of the SNPs are outliers. (E) A radial plot of the SNP weight versus the beta times its weight can show outlier SNPs (in green), plotted alongside the IVW estimate. All plots have been generated using the TwoSampleMR( 42 ) and RadialMR( 109 ) packages and publicly available summary statistics( 110 , 111 ) available through the IEU OpenGWAS project.( 43 )
