Figure 1.
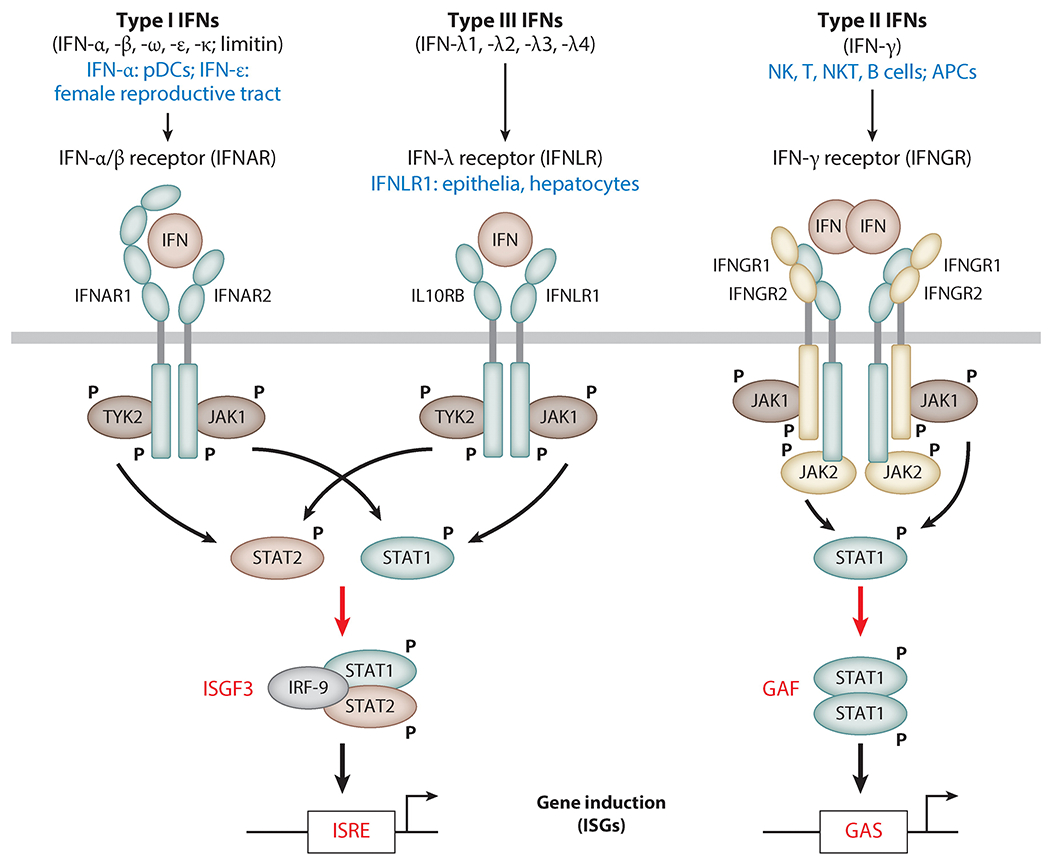
Major differences between the type I, II, and III IFN systems. Each type of IFN acts through its own cognate cell surface receptor. The Janus kinases JAK1, TYK2, and JAK2 phosphorylate STAT proteins and trigger their transcriptional activity. The three signaling systems are distinguished by their cell type–specific expression of IFNs or their receptor (blue), as well as by the different transcription factors they activate (red). Abbreviations: APC, antigen-presenting cell; GAS, gamma-activated site; IFN, interferon; ISG, interferon-stimulated gene; ISRE, IFN-stimulated response element; NK, natural killer; NKT, natural killer T; pDC, plasmacytoid dendritic cell. To download a PowerPoint slideshow illustrating further details about each IFN system, click the Interactive Figure button.
