Figure 2.
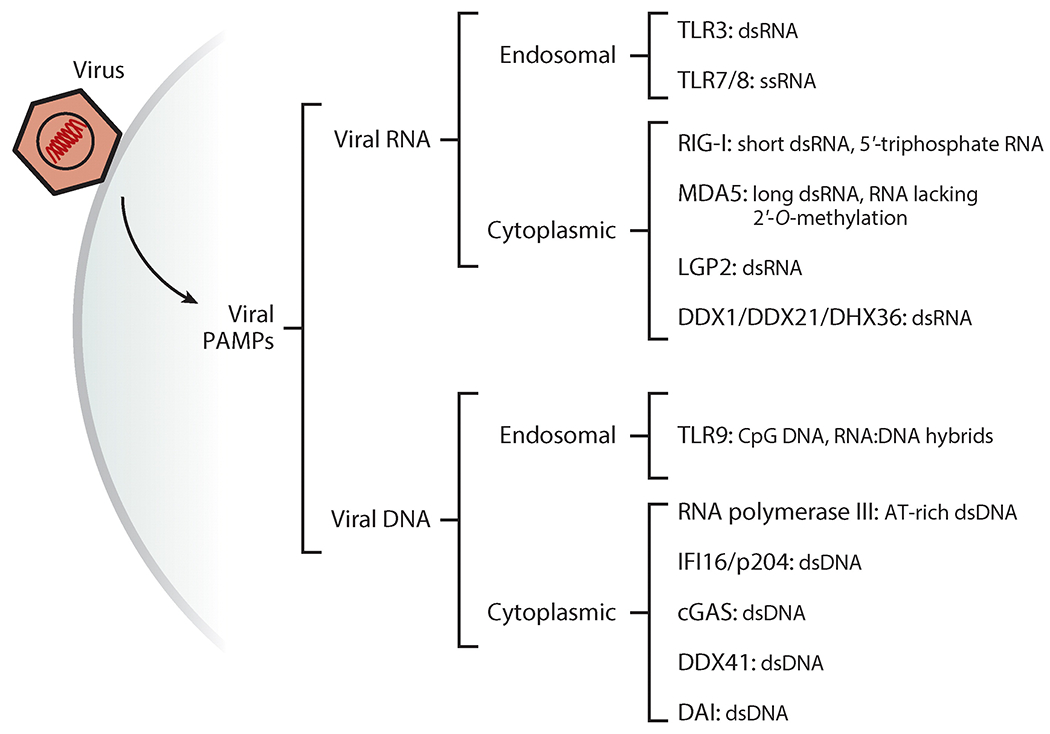
Cellular sensors detecting viral RNA and DNA. Viral nucleic acids are the key pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP) for cells to recognize the presence of viruses. A large number of sensor proteins (pattern-recognition receptors) bind specific forms of nucleic acids in endosomes and in the cytoplasm and trigger signaling to elicit innate immune responses such as the induction of interferons.
