Figure 3.
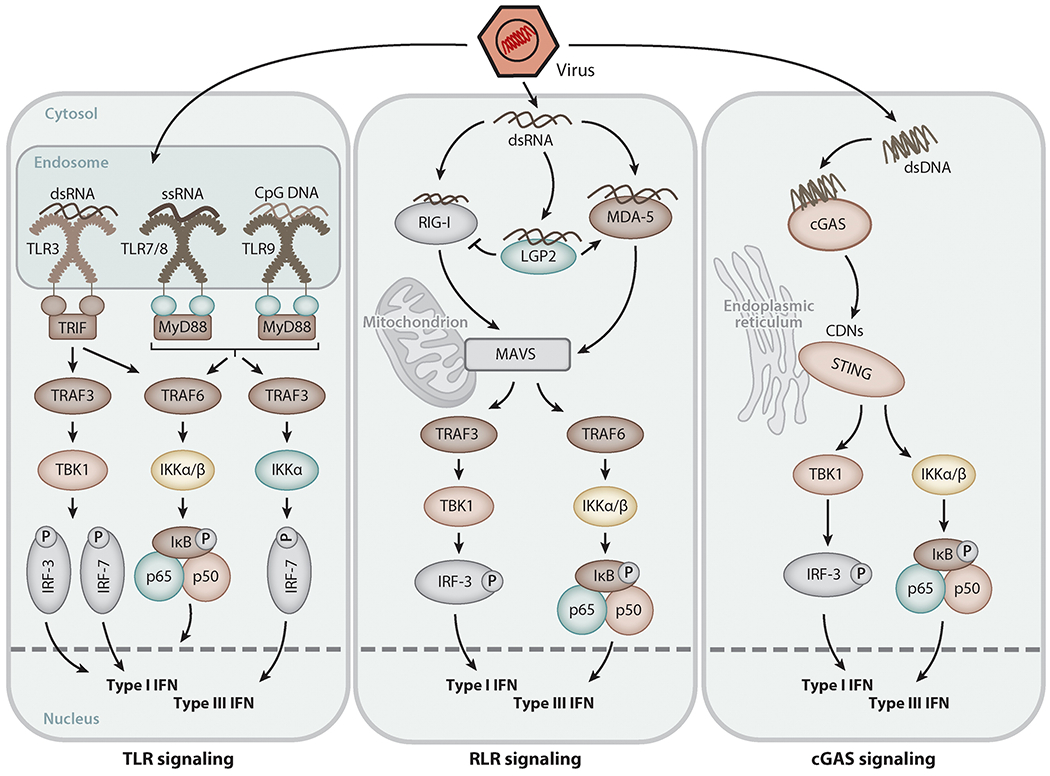
Signaling pathways for type I and III interferon (IFN) induction triggered by viral nucleic acids. Upon virus entry, viral RNA or DNA in endosomes or the cytoplasm is detected by receptor proteins [e.g., Toll-like receptors (TLRs), RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs), cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)], which trigger signaling via adapter proteins such as TRIF, MyD88, MAVS, and STING to activate transcription factors of the IRF family as well as NF-κB, leading to induced transcription of the type I and type III IFN genes.
