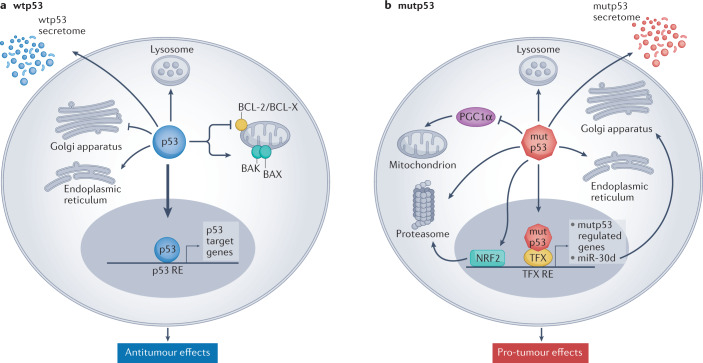
Fig. 1. Tumour-suppressive effects of wild-type p53 and oncogenic effects of mutant p53.
a | Wild-type p53 (wtp53) acts predominantly as a transcription factor to restrict cancer cell proliferation and survival. Many non-transcriptional effects are also involved. Wtp53 can promote mitochondrially induced apoptosis by interacting with multi-domain members of the apoptosis regulator BCL-2 family (such as BCL-2 and BCL-X), unleashing the activity of pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins such as BAK and BAX. Wtp53 can also increase Ca2+ load upon stress, resulting in induction of apoptosis. Additionally, wtp53 is an important regulator of autophagy. b | Mutant p53 (mutp53) can modulate transcription by piggybacking on other transcription factors (TFX) and can also promote cancer by non-transcriptional mechanisms. Mutp53 can inhibit peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α (PGC1α), a master regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative phosphorylation. Moreover, in contrast to wtp53, mutp53 inhibits endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-induced apoptosis by modulating the unfolded protein response (UPR), which increases cell survival upon ER stress. Mutp53 also induces the transcription of many genes that encode proteasome subunits. This transcriptional activation, mediated by the binding of mutp53 to the transcription factor nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2), results in elevated proteasome activity and enhanced degradation of tumour suppressor proteins. Both wtp53 and mutp53 impinge on multiple cellular organelles and compartments, and can also elicit non cell-autonomous effects through secretion of various molecules, both soluble and those carried by exosome or extracellular vesicle. The presence of wtp53 inhibits the expression of Golgi scaffolding proteins, thus inhibiting secretory vesicle biogenesis in the Golgi apparatus, while mutp53 can modulate Golgi apparatus function by inducing microRNA miR-30d expression through interacting with the hypoxia responsive factor HIF1α. Consequently, miR-30d modulates tubulo-vesiculation of the Golgi apparatus, promoting vesicular trafficking and secretion. RE, response element.